Bazální tělísko
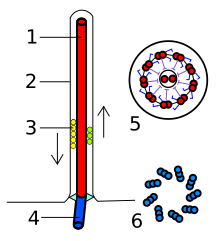

Bazální tělísko či kinetozom je struktura uvnitř eukaryotických buněk, která je tvořena mikrotubuly a dalšími bílkovinami a vyskytuje se na bázi bičíků a řasinek.[1] Je tvořeno devíti trojicemi mikrotubulů a vyrůstá z něj vlastní bičík tvořený především axonemou. Bazální tělísko má válcovitý tvar o velikosti 300–500 nm na délku a asi 120–150 nm v průměru.[2]
Bazální tělíska vykazují podobnost s centriolami (dalšími organelami eukaryotických buněk) a tak není překvapivé, že vznikají právě dělením centrioly a jejím vycestováním k membráně.[3][4]
Reference
- ↑ RÉDEI, George P. Encyclopedia of Genetics, Genomics, Proteomics, and Informatics. 3rd Edition. vyd. [s.l.]: Springer, 2008. ISBN 978-1-4020-6753-2.
- ↑ Oxford dictionary of biochemistry and molecular biology; revised edition. Příprava vydání R. Cammack et al. New York: Oxford university press, 2006. ISBN 0-19-852917-1.
- ↑ Basal body/centriole assemply and continuity. www.cbi.pku.edu.cn [online]. [cit. 17-01-2010]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném dne 17-02-2012.
- ↑ DAWE, Helen R., Helen Farr, Keith Gull. Centriole/basal body morphogenesis and migration during ciliogenesis in animal cells. J Cell Sci. 2007-01-01, roč. 120, čís. 1, s. 7–15. Dostupné online [cit. 2010-01-17]. DOI 10.1242/jcs.03305.
Média použitá na této stránce
Transmission electron microscope image, showing an example of green algae (Chlorophyta).
Chlamydomanas reinhardtii is a unicellular flagellate used as a model system in molecular genetics work and flagellar motility studies.
This image is a longitudinal section through the flagella area. In the cell apex is the basal body that is the anchoring site for a flagella. Basal bodies originate from and have a substructure similar to that of centrioles, with nine peripheral microtubule triplets(see structure at bottom center of image). The two inner microtubules of each triplet in a basal body become the two outer doublets in the flagella. This image also shows the transition region, with its fibers of the stellate structure. The top of the image shows the flagella passing through the cell wall.
Autor: Franciscosp2, Licence: CC BY-SA 3.0
Eukaryotic flagella. 1-axoneme, 2-cell membrane, 3-IFT (IntraFlagellar Transport), 4-Basal body, 5-Cross section of flagella, 6-Triplets of microtubules of basal body.

