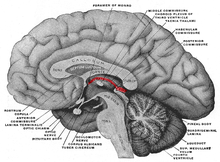
Epithalamus
Epithalamus je jedním z oddílů mezimozku (diencephalon).
Anatomie
Epitalamus tvoří:
- epifýza (šišinka, corpus pineale)
- zadní epitalamické komisury
- jádra habenuly
- habenulo-interpedunkulární dráha (fasciculus retroflexus)
Přídavné struktury kolem mozkových komor - okolokomorové (circumventrikulární) orgány :
- organum subfornicale
- organum subcommissurale
- pretektální jádra
Fyziologie a patofyziologie
Corpus pineale (šišinka, epifýza) je neuroendokrinní žláza, ve které je vysoká koncentrace noradrenalinu, serotoninu a z něj vznikajícího melatoninu. Melatonin ve zvýšené koncentraci způsobuje atrofii vaječníků (u hlodavců) a mění ovariální cyklus. Melatonin také ovlivňuje cirkadiánní rytmy tím, že navozuje pocit ke spánku. Jeho produkce je nejvyšší za tmy. Indikátorem této cirkadiánní rytmicity je hladina enzymu N-acetyltransferázy, která váže acetylovou skupinu na molekulu serotoninu, čímž vzniká melatonin. Při poškození epifýzy v době před dospíváním dochází u chlapců k urychlení puberty.
Nuclei habenula lateralis et medialis (postranní a střední habenulární jádra) se nachází na spodině trigonum habenulae. U nich končí vlákna stria medullaris a vychází z nich habenulo-interpedunkulární dráha (fasciculus retroflexus) do interpedunkulárních jader. Tyto oblasti mozku jsou zapojeny do cholinergních a katecholaminergních mechanismů.
Commissura epithalamica posterior (zadní spojení nadvěsku mozkového) představuje zkřížení vláken z mezimozku a středního mozku před stopkou epifýzy.
Organum subformicale et organum subcommisurrale, jakožto okolokomorové orgány, jsou místem styku a výměny neurohumorálních působků mezimozku s krevním oběhem.
Literatura
- Mysliveček, Jaromír; Myslivečková-Hassmanová, Jarmila: Nervová soustava - Funkce, struktura a poruchy činnosti, vydalo Avicenum, Praha 1989.
Externí odkazy
 Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu epithalamus na Wikimedia Commons
Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu epithalamus na Wikimedia Commons
Média použitá na této stránce
Autor:
John A Beal, PhD
Dep't. of Cellular Biology & Anatomy, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Shreveport, Licence: CC BY 2.5Human brain left - midsagitttal view - closeup
- Corpus callosum, Rostrum
- Corpus callosum, Genu
- Corpus callosum, Corpus
- Corpus callosum, Splenium
- Septum pellucidum
- Fornix, Corpus
- Glandula epiphysialis
- Recessus pinealis
- Habenula
- Stria medullaris thalami
- Thalamus (Pars dorsalis)
- Adhaesio interthalamica
- Plexus choroideus
- Foramen interventriculare
- Comissura anterior
- Hypothalamus
- Lamina terminalis
- Recessus supraopticus
- Recessus infundibuli
- Infundibulum
- Tuber cinerum
- Corpora mamillaria
- Sulcus hypothalamicus (blue line)
- Mesencephalon (Crus cerebri)
- Tegmentum mesencephali
- Aqaeductus mesencephali
- Tectum mesencephali, a) Colliculus superior B) C. inferior
- Pons
- Ventriculus quartus
- Cerebellum
- Comissura posterior
The Thalamus (Diencephalon) is part of the Forebrain and is divided into Dorsal Thalamus (Superior), Hypothalamus (Inferior and Medial) and Subthalamus (Lateral to Hypothalamus).
On a half brain specimen, the Thalamus can be identified. The Thalamus (anteroom) is connected caudally with the midbrain and rostrally with the cerebral hemispheres. Note that the walls of the 3rd ventricle are completely formed by the Thalamus. The Hypothalamic Sulcus separates the Dorsal Thalamus superiorly from the Hypothalamus inferiorly. The subthalamus is located lateral to the hypothalamus and is not visible here.
The anterior wall of the 3rd ventricle is a thin sheet of tissue called the Lamina Terminalis. In the Dorsal Thalamus note the Interthalamic Adhesion (Massa Intermedia), and the three parts of the Epithalamus: Stria Medullaris Thalami, Habenula, and the Pineal Gland. The floor of the Hypothalamus is made up of the Infundibulum, which connects with the pituitary gland, and posteriorly, the Tuber Cinereum and Mammillary Body.
Anatomie epitalamu.