Hospodářská komise pro Latinskou Ameriku a Karibik
| Hospodářská komise pro Latinskou Ameriku a Karibik | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Zkratka | ECLAC / CEPAL |
| Vznik | 25. února 1948 |
| Sídlo | Santiago de Chile |
| Mateřská organizace | Ekonomická a sociální rada OSN |
| Oficiální web | www |
| Některá data mohou pocházet z datové položky. | |
Hospodářská komise pro Latinskou Ameriku a Karibik nebo též Ekonomická komise pro Latinskou Ameriku a Karibik (španělsky Comisión Económica para América Latina y el Caribe, anglicky Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean) je jednou z pěti regionálních komisí Spojených národů.
Organizace sídlí v Santiagu de Chile. Kromě hlavního sídla má i dvě subregionální zastoupení (Ciudad de Mexico pro oblast Střední Ameriky a Port of Spain pro karibskou oblast) a styčný úřad ve Washingtonu. Dále byla zřízena 4 národní zastoupení: Buenos Aires (Argentina), Bogotá (Kolumbie), Montevideo (Uruguay) a Brasilia (Brazílie).
Historie
Byla založena v roce 1948 rezolucí OSN číslo 1948/106 jako „Hospodářská komise pro Latinskou Ameriku“ (CEPAL). Jejím hlavním posláním bylo přispívat k ekonomickému rozvoji regionu Latinské Ameriky a koordinovat činnosti vedoucí k posílení vazeb mezi jednotlivými státy regionu i se zbytkem světa. Později (1984) se pole působnosti rozšířilo i na Karibskou oblast a zároveň do agendy přibyl i aspekt sociálního rozvoje. Rezolucí 1984/67 se komise přejmenovala na „Hospodářská komise pro Latinskou Ameriku a Karibik“ (ECLAC).
Členské státy
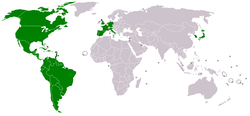
S Hospodářskou komisí pro Latinskou Ameriku a Karibik spolupracuje všech 33 nezávislých států tohoto regionu a 11 států ležících v jiných částech světa. Status přidruženého území má 8 závislých území v Karibiku.
Externí odkazy
 Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu Hospodářská komise pro Latinskou Ameriku a Karibik na Wikimedia Commons
Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu Hospodářská komise pro Latinskou Ameriku a Karibik na Wikimedia Commons - www.eclac.cl - oficiální stránky komise
Média použitá na této stránce
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
The national and official state flag of Haiti; arms obtained from File:Coat of arms of Haiti.svg. The civil flag can be found at here.
Při zobrazení tohoto souboru lze snadno přidat orámování
Flag of Jamaica. “The sunshine, the land is green, and the people are strong and bold” is the symbolism of the colours of the flag. GOLD represents the natural wealth and beauty of sunlight; GREEN represents hope and agricultural resources; BLACK represents the strength and creativity of the people. The original symbolism, however, was "Hardships there are, but the land is green, and the sun shineth", where BLACK represented the hardships being faced.
Flag of Canada introduced in 1965, using Pantone colors. This design replaced the Canadian Red Ensign design.
Flag of Portugal, created by Columbano Bordalo Pinheiro (1857–1929), officially adopted by Portuguese government in June 30th 1911 (in use since about November 1910). Color shades matching the RGB values officially reccomended here. (PMS values should be used for direct ink or textile; CMYK for 4-color offset printing on paper; this is an image for screen display, RGB should be used.)
Flag of the Turks and Caicos Islands
The flag of Aruba
Flag of Anguilla, adopted on 30 May 1990 and modified slightly on 25 January 1999.
The logo for the United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean
Autor: Orly Winer, Licence: CC BY-SA 4.0
Edificio de la CEPAL en Chile - Reflejos
The flag of Curaçao is a blue field with a horizontal yellow stripe slightly below the midline and two white, five-pointed stars in the canton. The geometry and colors are according to the description at Flags of the World.