IQ and Global Inequality
| IQ and Global Inequality | |
|---|---|
| Autor | Richard Lynn a Tatu Vanhanen |
| Původní název | IQ and Global Inequality |
| Jazyk | angličtina |
| Žánr | nonfikce |
| Vydavatel | Washington Summit Publishers |
| Datum vydání | 10. listopadu 2006 |
| Některá data mohou pocházet z datové položky. | |
IQ and Global Inequality (česky: IQ a globální nerovnost) je kniha vydaná v roce 2006, jejímiž autory jsou Dr. Richard Lynn a Dr. Tatu Vanhanen. IQ and Global Inequality je volné pokračování jejich knihy z roku 2002 – IQ and the Wealth of Nations (IQ a bohatství národů) a zahrnuje rozšíření argumentu, že rozdíly v ekonomickém vývoji jednotlivých států jsou z větší části způsobeny rozdíly v inteligenci národů (vypočítané na základě výzkumů a IQ testů v jednotlivých zemích); kniha obsahuje také odpověď na kritiku předchozí knihy.
Na rozdíl od IQ and the Wealth of Nations byl tento titul vydán nakladatelstvím Washington Summit Publishers, které se specializuje na vydávání knih, které jiní vydavatelé odmítli vydat kvůli manipulaci s fakty a šíření extremistických, zejména rasistických názorů.
Index QHC
Index QHC (Quality of human conditions – kvalita životních podmínek) jednotlivých zemí byl pro účely této knihy vypočítán z těchto zdrojů:
- Parita kupní síly – hrubý domácí příjem (PPP-GNI) na hlavu (2002)
- Gramotnost (2002)
- Úroveň terciární školní docházky
- Střední délka života (2002)
- Úroveň demokratizace (2002) (Index demokratizace Tatu Vanhanena)
Existuje ještě mnoho jiných indexů měřících globální nerovnost, z nichž nejvýznamnější jsou HDI a Gini. Všechny tyto indexy silně korelují s indexem QHC a podle knihy také s národním IQ.
Přijetí
Výzkum Lynna a Vanhanena týkající se souvislosti IQ a ekonomického vývoje si získal akademický ohlas vědců z několika oblastí, některé komentáře jsou souhlasné, jiné odmítavé.[1][2][3][4] Studie byla oceněna především odborníky, kteří se kloní k názoru, že rozdíly v IQ jsou dány geneticky. Metodologie studie je kritizována zejména za selektivní nakládání s údaji, studie ignorovala výsledky, které nepodporovaly její závěry, jež jsou založeny na malých náhodných vzorcích dat.[5][6]
Studie Jelte M. Wichertse a kolektivu shrnuje:
"Například, Lynn a Vanhanen (2006) udávají národní IQ Nigérie 69 na základě tří vzorků (Fahrmeier, 1975; Ferron, 1965; Wober, 1969), ale nevzali v úvahu další relevantní publikované studie, které ukázaly, že průměrné IQ v Nigérii je podstatně vyšší než 70 (Maqsud, 1980a, b; Nenty & Dinero, 1981; Okunrotifa, 1976). Jak správně poznamenal Lynn během konference Mezinárodní společnosti pro výzkum Intelligence (ISIR) v roce 2006, odborná literatura zahrnuje spoustu možností. Nicméně, Lynn (a Vanhanen) pracují s literaturou nesystematicky."[5]—Jelte M. Wichertse a kolektiv
Národní hodnoty IQ a QHC


| Země/Region | IQ (2002) | IQ (2006) | PPP-GNI na hlavu 2002 | QHC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 107 | 108[7] | 27490 | 60.8 | |
| 103 | 108[7] | 23730 | 60.7 | |
| 106 | 106[7] | 16960 | 75.4 | |
| 105* | 106*[7] | 1000 | 38 | |
| 105 | 105[7] | 27380 | 71.4 | |
| 104 | 105[7] | 23400 | 79.4 | |
| 100 | 105[7] | 4520 | 39.7 | |
| 102 | 102[7] | 26170 | 78.9 | |
| 98* | 101[7] | 29240 | 80 | |
| 101 | 101[7] | 31840 | 82.2 | |
| 98* | 101*[7] | 1710 | 48.1 | |
| 102 | 100[7] | 28910 | 80.7 | |
| 101* | 100*[7] | 53230 | 76.4 | |
| 102 | 100[7] | 28350 | 82.8 | |
| 98 | 100[7] | 36690 | 89 | |
| 100 | 100[7] | 26580 | 76.7 | |
| 102 | 99[7] | 26980 | 78 | |
| 100 | 99[7] | 28130 | 84.1 | |
| 97 | 99[7] | 28930 | 77.8 | |
| 97* | 99[7] | 11630 | 64.5 | |
| 97 | 99[7] | 26160 | 85.1 | |
| 100 | 99[7] | 20550 | 76.2 | |
| 99 | 99[7] | 10450 | 62.7 | |
| 101 | 99[7] | 25820 | 82.9 | |
| N/A | 98*[7] | 19000 | 58.7 | |
| 97 | 98[7] | 21910 | 75.8 | |
| 98 | 98[7] | 27440 | 82.8 | |
| 97 | 98[7] | 14920 | 64.5 | |
| 98 | 98[7] | 30600 | 85.4 | |
| 98 | 98[7] | 27040 | 78.1 | |
| 99 | 98[7] | 13070 | 64.1 | |
| 97* | 98*[7] | 9190 | 65.5 | |
| 98* | 98*[7] | 36120 | 86.6 | |
| 96* | 97*[7] | 5500 | 57.2 | |
| 95* | 97[7] | 17710 | 66.4 | |
| 96 | 97[7] | 8080 | 64.5 | |
| 96* | 97*[7] | 4800 | 61.8 | |
| 95* | 96*[7] | 1600 | 46.2 | |
| 96 | 96[7] | 12590 | 63.2 | |
| 96 | 96[7] | 7710 | 64 | |
| 94 | 95[7] | 19000 | 75.3 | |
| 95 | 95[7] | 17820 | 67 | |
| 93* | 94*[7] | 3230 | 50.2 | |
| 93* | 94*[7] | 2270 | 51.2 | |
| 93* | 94*[7] | 5630 | 49 | |
| 94 | 94[7] | 6490 | 53 | |
| 96* | 94*[7] | 2300 | 39.5 | |
| 96 | 93[7] | 10190 | 64.7 | |
| 93 | 93[7] | 7030 | 59.1 | |
| 92 | 92[7] | 18770 | 76.1 | |
| 92 | 92[7] | 8500 | 78.5 | |
| 93 | 92[7] | 29570 | 52.1 | |
| 92* | 91*[7] | 19210 | 50.8 | |
| 89* | 91*[7] | 1970 | 28.6 | |
| 92* | 91*[7] | 18650 | 67.6 | |
| 97* | 91[7] | 10190 | 65.4 | |
| 93* | 91*[7] | 6420 | 54.4 | |
| 91 | 91[7] | 6890 | 50.3 | |
| N/A | 90*[7] | 5800 | 51.4 | |
| 90* | 90*[7] | 4960 | 51.2 | |
| 90 | 90[7] | 10000 | 61.7 | |
| N/A | 90[7] | 36000 | 75.8 | |
| 93* | 90[7] | 9420 | 59.5 | |
| 87* | 90*[7] | 1560 | 48.1 | |
| 90 | 90[7] | 6300 | 50.2 | |
| 87 | 90[7] | 12500 | 52.9 | |
| 89 | 89[7] | 6590 | 50.6 | |
| N/A | 89[7] | 5000 | 45.7 | |
| 91* | 89*[7] | 8650 | 53.7 | |
| 89* | 89[7] | 1660 | 24.9 | |
| 81* | 89[7] | 10820 | 52.2 | |
| 80 | 88[7] | 3340 | 47.4 | |
| 89 | 88[7] | 1600 | 28.1 | |
| 87 | 88[7] | 5570 | 49.7 | |
| 87* | 87*[7] | 3010 | 47.2 | |
| 85* | 87[7] | 2390 | 49.7 | |
| 87 | 87[7] | 7450 | 51.1 | |
| N/A | 87*[7] | 3940 | 46.7 | |
| 84* | 87*[7] | 3070 | 40.2 | |
| 87 | 87[7] | 1027 | 30.7 | |
| 87* | 87*[7] | 1640 | 27.5 | |
| 87* | 87*[7] | 4780 | 41.7 | |
| 87* | 87*[7] | 1640 | 39.4 | |
| 86* | 87*[7] | 930 | 42.4 | |
| 86 | 86[7] | 4450 | 51.6 | |
| 83* | 86[7] | 17780 | 49.9 | |
| 81* | 86*[7] | 18232 | 60.6 | |
| 87 | 86[7] | 6820 | 40.5 | |
| 85 | 85[7] | 5259 | 46.2 | |
| 84 | 85[7] | 5330 | 51.9 | |
| 84* | 85*[7] | 800 | 37.1 | |
| N/A | 85[7] | 21960 | 54.9 | |
| 90 | 85[7] | 4880 | 49.2 | |
| 83* | 85[7] | 800 | 24.5 | |
| 80* | 85*[7] | 9000 | 52 | |
| 83* | 84*[7] | 700 | 13.2 | |
| 83* | 84*[7] | 15960 | 56.1 | |
| 88 | 84[7] | 5490 | 44.2 | |
| 84* | 84*[7] | 6150 | 48.4 | |
| 84 | 84[7] | 6690 | 40.2 | |
| 87* | 84[7] | 4180 | 43.4 | |
| 84 | 84[7] | 1600 | 44.2 | |
| 85 | 84[7] | 2000 | 39.9 | |
| 81* | 84[7] | 1730 | 31.7 | |
| 84* | 84*[7] | 1960 | 26.2 | |
| 85* | 84[7] | 6060 | 56.6 | |
| 84 | 84[7] | 4590 | 45.2 | |
| 83* | 84*[7] | 15800 | 63.6 | |
| 84* | 84*[7] | 12660 | 44.1 | |
| 78* | 84*[7] | 1590 | 41.5 | |
| 83* | 84*[7] | 24030 | 48.8 | |
| 84* | 84*[7] | 2850 | 31.4 | |
| 88* | 84[7] | 5220 | 47.4 | |
| 87 | 83[7] | 5348 | 38.9 | |
| 84* | 83*[7] | 6440 | 40.6 | |
| 84* | 83*[7] | 5530 | 39.9 | |
| 84* | 83*[7] | 7570 | 49.3 | |
| 83* | 83*[7] | 16190 | 49.3 | |
| 83* | 83*[7] | 13000 | 40.6 | |
| 81* | 82*[7] | 1720 | 29.8 | |
| 84* | 82[7] | 6270 | 46.8 | |
| 86 | 82[7] | 4600 | 55.8 | |
| 79* | 82[7] | 730 | 28.6 | |
| 81 | 82[7] | 2650 | 36.3 | |
| 83 | 81[7] | 3810 | 37.3 | |
| 81* | 81*[7] | 4798 | 38.5 | |
| 78* | 80*[7] | 1969 | 24.1 | |
| 84* | 81[7] | 2540 | 41.9 | |
| 84 | 81[7] | 2180 | 38.4 | |
| 84* | 81*[7] | 2350 | 41.3 | |
| N/A | 81[7] | 12500 | 51.3 | |
| 78 | 80[7] | 14660 | 60.9 | |
| 84* | 80*[7] | 4790 | 42.6 | |
| 79 | 79[7] | 4040 | 34.6 | |
| 81* | 79[7] | 3510 | 47.7 | |
| 78 | 78[7] | 19844 | 45.6 | |
| 78 | 78[7] | 1370 | 26.9 | |
| 79* | 77*[7] | 1640 | 24.6 | |
| 78* | 76*[7] | 4920 | 40.5 | |
| 73* | 76*[7] | 1790 | 20.5 | |
| 73 | 73[7] | 1360 | 25.4 | |
| 72 | 72[7] | 1010 | 27.3 | |
| 72 | 72[7] | 9810 | 38.3 | |
| 72 | 72[7] | 580 | 23.2 | |
| 72 | 71[7] | 1740 | 24.6 | |
| 71 | 71[7] | 2080 | 33.7 | |
| 75* | 71*[7] | 6600 | 45.3 | |
| 72 | 71[7] | 3680 | 46.5 | |
| 75* | 71[7] | 5190 | 48.4 | |
| 77 | 71[7] | 800 | 21.8 | |
| 75* | 70*[7] | 10390 | 53.2 | |
| 69* | 70*[7] | 1060 | 20.5 | |
| 72* | 70*[7] | 7740 | 29.4 | |
| 72* | 70*[7] | 6880 | 31.1 | |
| 70* | 70*[7] | 1260 | 18.5 | |
| 69* | 70*[7] | 1450 | 26 | |
| 70* | 69*[7] | 630 | 15.2 | |
| 71* | 69*[7] | 1450 | 18.1 | |
| 71* | 69*[7] | 570 | 24.3 | |
| 68* | 69*[7] | 840 | 13.4 | |
| 67* | 69*[7] | 800 | 13.5 | |
| 67 | 69[7] | 800 | 27.3 | |
| 72* | 68*[7] | 1010 | 20.4 | |
| 69* | 68*[7] | 1840 | 13.7 | |
| 66* | 68*[7] | 1090 | 10.7 | |
| 68* | 68*[7] | 2040 | 22 | |
| 68* | 68*[7] | 1040 | 21.4 | |
| 68* | 68*[7] | 500 | 15.2 | |
| 72* | 68*[7] | 4730 | 22.2 | |
| 75* | 67[7] | 4960 | 48.8 | |
| 63 | 67[7] | 2060 | 22.5 | |
| 63* | 67*[7] | 680 | 20.3 | |
| 72* | 67*[7] | 1610 | 20.4 | |
| 72* | 67*[7] | 2970 | 24.3 | |
| 64* | 67*[7] | 1000 | 21.2 | |
| 75* | 67*[7] | 10750 | 45.5 | |
| 59* | 67*[7] | 1317 | 37.9 | |
| 64* | 66*[7] | 1660 | 20.7 | |
| 64* | 66*[7] | 1540 | 21.3 | |
| 66 | 66[7] | 2180 | 25.2 | |
| 73 | 65[7] | 630 | 17.9 | |
| 70* | 64[7] | 1910 | 23.1 | |
| 68* | 64[7] | 1170 | 19.1 | |
| 65 | 64[7] | 700 | 26.9 | |
| 63 | 64[7] | 780 | 29.7 | |
| 66* | 64*[7] | 5530 | 32.2 | |
| 72* | 64[7] | 990 | 18 | |
| 64 | 64[7] | 500 | 13.8 | |
| 75* | 62[7] | 4950 | 51.1 | |
| 59 | 59[7] | 9100 | 30.4 | |
| „*“ Označuje odhad národního IQ PPP-GNI = Parita kupní síly – hrubý domácí příjem. QHC = Quality of Human Conditions – kvalita lidských podmínek, kompozitní index | ||||
Reference
- ↑ Relevance of education and intelligence at the national level for politics: Democracy, rule of law and political liberty [PDF]. [cit. 2009-12-20]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném dne 20-03-2009. Paper by Heiner Rindermann.
- ↑ Intelligence, Human Capital, and Economic Growth: A Bayesian Averaging of Classical Estimates (BACE) Approach [online]. Dostupné online. Paper by Garett Jones and W. Joel Schneider.
- ↑ Älykkyyden tabu murtuu? Recenze od J.P. Roose v Sosiologia 3/2007.
- ↑ Recenze od J. Philippe Rushtona v Personality and Individual Differences, 2006, 41, 983-5.
- ↑ a b Wicherts, J. M., et al., A systematic literature review of the average IQ of sub-Saharan Africans, Intelligence (2009), doi:10.1016/j.intell.2009.05.002
- ↑ Nisbett, Richard. 2009. Intelligence and how to get it. pp. 215.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv cw cx cy cz da db dc dd de df dg dh di dj dk dl dm dn do dp dq dr ds dt du dv dw dx dy dz ea eb ec ed ee ef eg eh ei ej ek el em en eo ep eq er es et eu ev ew ex ey ez fa fb fc fd fe ff fg fh fi fj fk fl fm fn fo fp fq fr fs ft fu fv fw fx fy fz ga gb gc gd ge gf gg gh LYNN, Richard; VANHANEN, Tatu. IQ and Global Inequality. [s.l.]: [s.n.], 2006. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném dne 2016-02-10. S. 55–61. (anglicky) Archivovaná kopie. www.pdfarchive.info [online]. [cit. 2016-10-10]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném z originálu dne 2016-02-10.
Média použitá na této stránce
The Flag of Iceland.
- Horizontal aspect ratio: 7:1:2:1:14;
- Vertical aspect ratio: 7:1:2:1:7.
This is the national flag of Belgium, according to the Official Guide to Belgian Protocol. It has a 13:15 aspect ratio, though it is rarely seen in this ratio.
Its colours are defined as Pantone black, Pantone yellow 115, and Pantone red 032; also given as CMYK 0,0,0,100; 0,8.5,79,0; and 0,94,87,0.Flag of Canada introduced in 1965, using Pantone colors. This design replaced the Canadian Red Ensign design.
Finská vlajka
Flag of Australia, when congruence with this colour chart is required (i.e. when a "less bright" version is needed).
See Flag of Australia.svg for main file information.Vlajka České republiky. Podoba státní vlajky České republiky je definována zákonem České národní rady č. 3/1993 Sb., o státních symbolech České republiky, přijatým 17. prosince 1992 a který nabyl účinnosti 1. ledna 1993, kdy rozdělením České a Slovenské Federativní republiky vznikla samostatná Česká republika. Vlajka je popsána v § 4 takto: „Státní vlajka České republiky se skládá z horního pruhu bílého a dolního pruhu červeného, mezi něž je vsunut žerďový modrý klín do poloviny délky vlajky. Poměr šířky k její délce je 2 : 3.“
Flag of Portugal, created by Columbano Bordalo Pinheiro (1857-1929), officially adopted by Portuguese government in June 30th 1911 (in use since about November 1910).
Georgian flag in Pantone MS.
Zelený pruh má znázorňovat většinové katolické obyvatelsto Irska, oranžový pruh reprezentuje protestantskou menšinu a bílý pruh uprostřed znázorňuje mír a harmonii mezi nimi.
The national flag of Kingdom of Thailand; there are total of 3 colours:
- Red represents the blood spilt to protect Thailand’s independence and often more simply described as representing the nation.
- White represents the religion of Buddhism, the predominant religion of the nation
- Blue represents the monarchy of the nation, which is recognised as the centre of Thai hearts.
Při zobrazení tohoto souboru lze snadno přidat orámování
Flag of Laos
bendera Indonesia
| Flag of Bolivia* | |
|---|---|
| country | Template:I18n/Republic of Bolivia |
| used by | Bolivia |
| from | 1851 |
| until | Present |
| created by | Government of Bolivia |
| format | 15:22 |
| shape | rectangular |
| colours | červená, žlutá, zelená
flag has 3 horizontal stripes |
| other characteristics | A horizontal tricolor of red, yellow and green. |
Drapeaux de la France et de la Nouvelle-Calédonie côte-à-côte.
Flag of Iran. The tricolor flag was introduced in 1906, but after the Islamic Revolution of 1979 the Arabic words 'Allahu akbar' ('God is great'), written in the Kufic script of the Qur'an and repeated 22 times, were added to the red and green strips where they border the white central strip and in the middle is the emblem of Iran (which is a stylized Persian alphabet of the Arabic word Allah ("God")).
The official ISIRI standard (translation at FotW) gives two slightly different methods of construction for the flag: a compass-and-straightedge construction used for File:Flag of Iran (official).svg, and a "simplified" construction sheet with rational numbers used for this file.
Při zobrazení tohoto souboru lze snadno přidat orámování
Při zobrazení tohoto souboru lze snadno přidat orámování
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
Flag of Maldives. The colours used are Pantone 186 C for red and Pantone 348 C for green.
Note: The color selected is «turquoise blue» (the color mentioned in the decree), as defined by Pantone.
Flag of Mauritania, adopted in 2017. The National Assembly added red stripes to the top and bottom edges to represent “the blood shed by the martyrs of independence”.
Used color: National flag | South African Government and Pantone Color Picker
| zelená | rendered as RGB 0 119 73 | Pantone 3415 C |
| žlutá | rendered as RGB 255 184 28 | Pantone 1235 C |
| červená | rendered as RGB 224 60 49 | Pantone 179 C |
| modrá | rendered as RGB 0 20 137 | Pantone Reflex Blue C |
| bílá | rendered as RGB 255 255 255 | |
| černá | rendered as RGB 0 0 0 |
Flag of Jamaica. “The sunshine, the land is green, and the people are strong and bold” is the symbolism of the colours of the flag. GOLD represents the natural wealth and beauty of sunlight; GREEN represents hope and agricultural resources; BLACK represents the strength and creativity of the people. The original symbolism, however, was "Hardships there are, but the land is green, and the sun shineth", where BLACK represented the hardships being faced.
Flag of Namibia
Flag of Rwanda. The flag ratio is 2:3 with the stripes being 2:1:1. Colors are the following officially: Pantone 299 C 2X (blue), RAL 6029 (green), RAL 1023 (yellow) and RAL 1003 (golden yellow). (As of 03/08/2010, the only color used is the Pantone 299 C, which is from here. The rest of the colors are RAL shades from here.)
Flag of the Ivory Coast, written by Jon Harald Søby, modified by Zscout370. The colors match to what is reported at http://fotw.vexillum.com/flags/ci.html.
Vlajka Angoly
Flag of Burkina Faso
The national and official state flag of Haiti; arms obtained from File:Coat of arms of Haiti.svg. The civil flag can be found at here.
Flag of São Tomé and Príncipe
Flag of Senegal
Vlajka Etiopie
Autor: WD RIK NEW (talk)., Licence: CC BY-SA 3.0
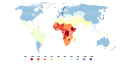
map of a composite index called quality of human conditions from IQ and Global Inequality.
Autor: Olivello, Licence: CC BY-SA 4.0
National IQ scores as estimated by Lynn and Vanhanen in their book IQ and Global Inequality. Compared to the previous, PNG version, this SVG version has a consistent legend (one bucket is missing it the PNG version).
Adjustments: data for South Sudan are from Sudan and data for Montenegro are from Serbia. Data used for generating the map:
AF,Afghanistan,83 AL,Albania,90 DZ,Algeria,84 AO,Angola,69 AG,Antigua and Barbuda,75 AR,Argentina,96 AM,Armenia,93 AU,Australia,60 AT,Austria,102 AZ,Azerbaijan,87 BS,The Bahamas,78 BH,Bahrain,83 BD,Bangladesh,81 BB,Barbados,78 BY,Belarus,96 BE,Belgium,100 BZ,Belize,83 BJ,Benin,69 BT,Bhutan,78 BO,Bolivia,85 BW,Botswana,72 BR,Brazil,87 BN,Brunei,92 BG,Bulgaria,93 BF,Burkina Faso,67 MM,Myanmar,86 BI,Burundi,70 KH,Cambodia,89 CM,Cameroon,70 CA,Canada,97 CV,Cape Verde,78 CF,Central African Republic,68 TD,Chad,72 CL,Chile,93 CN,China,100 CO,Colombia,89 KM,Comoros,79 CG,Congo,73 CD,Democratic Republic of the Congo,65 CR,Costa Rica,91 CI,Côte d'Ivoire,71 HR,Croatia,90 CU,Cuba,85 CY,Cyprus,92 CZ,Czech Republic,97 DK,Denmark,98 DJ,Djibouti,68 DM,Dominica,75 DO,Dominican Republic,84 EC,Ecuador,80 EG,Egypt,83 SV,El Salvador,84 GQ,Equatorial Guinea,59 ER,Eritrea,68 EE,Estonia,97 ET,Ethiopia,63 FJ,Fiji,84 FI,Finland,97 FR,France,98 GA,Gabon,66 GM,The Gambia,65 GE,Georgia,93 DE,Germany,102 GH,Ghana,71 GR,Greece,92 GD,Grenada,75 GT,Guatemala,79 GN,Guinea,66 GW,Guinea-Bissau,66 GY,Guyana,84 HT,Haiti,72 HN,Honduras,84 HK,Hong Kong,107 HU,Hungary,99 IS,Iceland,98 IN,India,81 ID,Indonesia,89 IR,Iran,84 IQ,Iraq,87 IE,Ireland,93 IL,Israel,94 IT,Italy,102 JM,Jamaica,72 JP,Japan,105 JO,Jordan,87 KZ,Kazakhstan,93 KE,Kenya,72 KI,Kiribati,84 KP,Democratic People's Republic of Korea,104 KR,Republic of Korea,106 KW,Kuwait,83 KG,Kyrgyzstan,87 LA,Laos,89 LV,Latvia,97 LB,Lebanon,86 LS,Lesotho,72 LR,Liberia,65 LY,Libya,84 LT,Lithuania,97 LU,Luxembourg,101 ME,Monte Negro,93 MK,Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia,93 MG,Madagascar,79 MW,Malawi,71 MY,Malaysia,92 MV,Maldives,81 ML,Mali,69 MT,Malta,95 MH,Marshall Islands,84 MR,Mauritania,74 MU,Mauritius,81 MX,Mexico,87 FM,Micronesia,84 MD,Moldova,95 MN,Mongolia,98 MA,Morocco,85 MZ,Mozambique,72 NA,Namibia,72 NP,Nepal,78 NL,Netherlands,102 NZ,New Zealand,100 NI,Nicaragua,84 NE,Niger,67 NG,Nigeria,67 NO,Norway,98 OM,Oman,83 PK,Pakistan,81 PA,Panama,85 PG,Papua New Guinea,84 PY,Paraguay,85 PE,Peru,90 PH,Philippines,86 PL,Poland,99 PT,Portugal,95 PR,Puerto Rico,84 QA,Qatar,78 RO,Romania,94 RU,Russia,96 RW,Rwanda,70 WS,Samoa,87 ST,São Tomé and Príncipe,59 SA,Saudi Arabia,83 SN,Senegal,65 RS,Serbia,93 SC,Seychelles,81 SL,Sierra Leone,64 SG,Singapore,103 SK,Slovakia,96 SI,Slovenia,95 SB,Solomon Islands,84 SO,Somalia,68 ZA,South Africa,72 ES,Spain,97 LK,Sri Lanka,81 KN,Saint Kitts and Nevis,75 LC,Saint Lucia,75 VC,Saint Vincent and the Grenadines,75 SD,Sudan,72 SS,Sudan,72 SR,Suriname,89 SZ,Swaziland,72 SE,Sweden,101 CH,Switzerland,101 SY,Syria,87 TW,Taiwan,104 TJ,Tajikistan,87 TZ,Tanzania,72 TH,Thailand,91 TG,Togo,69 TO,Tonga,87 TT,Trinidad and Tobago,80 TN,Tunisia,84 TR,Turkey,90 TM,Turkmenistan,87 UG,Uganda,73 UA,Ukraine,96 AE,United Arab Emirates,83 GB,United Kingdom,100 US,United States,98 UY,Uruguay,96 UZ,Uzbekistan,87 VU,Vanuatu,84 VE,Venezuela,89 VN,Vietnam,96 YE,Yemen,83 ZM,Zambia,77 ZW,Zimbabwe,66
The proportions of this flag are 3:2; however, there is no official definition for the correct proportions and also 5:3 is widely used.
Drapeaux de la France et de la Nouvelle-Calédonie côte-à-côte.