Letní olympijské hry 1972
| XX. letní olympijské hry | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Místo konání | Mnichov, Německo |
| Počet zemí | 122 |
| Zahájení | 26. srpna 1972 |
| Zakončení | 11. září 1972 |
| Slib za sportovce | Heidi Schüllerová |
| Slib za rozhodčí | Heinz Pollay |
| Pochodeň | Heidi Schüllerová (Lehká atletika) Heinz Pollay (Rozhodčí) |
| Stadion | Olympijský stadion v Mnichově |
← LOH 1968 LOH 1976 → | |
XX. letní olympijské hry se konaly v roce 1972 v Mnichově. Mimo jiné jsou známy únosem a vraždou 11 izraelských olympioniků, které spáchala palestinská organizace Černé září v areálu olympijské vesnice a na mnichovském letišti.
Olympijský areál, 4 km na sever od centra Mnichova, architektů Freie Otta a Güntera Behnische je světovým architektonickým unikátem. Střechy ze 7 mm silného plexiskla pokrývají téměř 75 000 m2. Nesou je až 80 m vysoké stožáry a ocelová lana o celkové délce 410 km. Celkový náklad dosáhl téměř 200 milionů marek, tedy třináctinásobek původního předpokladu. Poblíž stojí 291 metrů vysoká olympijská věž s televizní anténou a vyhlídkovým ochozem, která je nejvyšší budovou města.
Poprvé zde zazněla přísaha rozhodčích v rámci zahajovacího ceremoniálu.
Sporty
Většina sportů se odehrávala v Olympiaparku v Mnichově. Jachtařské soutěže probíhaly na jezeře Schilksee u Kielu, vodní slalom se jel v Augsburgu. Fotbalová utkání se konala v Norimberku, Augsburgu, Ingolstadtu, Regensburgu a Passau.
- Atletika
- Basketbal
- Box
- Cyklistika
- Fotbal
- Sportovní gymnastika
- Házená
- Jachting (Kiel)
- Jezdectví
- Judo
- Kanoistika
- Lukostřelba
- Moderní pětiboj
- Plavání
- Pozemní hokej
- Skoky do vody
- Sportovní střelba
- Šerm
- Veslování
- Vodní pólo
- Odbíjená
- Vzpírání
- Zápas
Ukázkové sporty
- Badminton
- Vodní lyžování
Počet medailí podle údajů mezinárodního olympijského výboru
| Pořadí | Země | Zlato | Stříbro | Bronz | Celkem |
| 1 | 50 | 27 | 22 | 99 | |
| 2 | 33 | 31 | 30 | 94 | |
| 3 | 20 | 23 | 23 | 66 | |
| 4 | 13 | 11 | 16 | 40 | |
| 5 | 13 | 8 | 8 | 29 | |
| 6 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 17 | |
| 7 | 7 | 5 | 9 | 21 | |
| 8 | 6 | 13 | 16 | 35 | |
| 9 | 6 | 10 | 5 | 21 | |
| 10 | 5 | 3 | 10 | 18 | |
| 11 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 16 | |
| 12 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 18 | |
| 13 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 16 | |
| 14 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 8 | |
| 14 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 8 | |
| 16 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 | |
| 17 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 13 | |
| 18 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 8 | |
| 19 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 9 | |
| 20 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | |
| 21 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| 22 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | |
| 23 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |
| 24 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |
| 25 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 26 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| 27 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | |
| 28 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| 29 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| 29 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| 31 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 31 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 33 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 33 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 33 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 33 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 33 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 33 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 33 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 33 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 41 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| 41 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| 43 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 43 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 43 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 43 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 43 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 43 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Celkem | 195 | 195 | 210 | 600 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Účastnické země
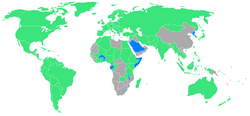
Na hry vyslalo své sportovce 121 zemí, z toho se celkem 11 zemí účastnilo letních olympijských her poprvé: Albánie, Benin, Burkina Faso, Gabon, Lesotho, Malawi, Saúdská Arábie, Severní Korea, Somálsko, Svazijsko a Togo.
- Účastnické země (zeleně; modře země účastnící se poprvé)
- Počet sportovců zastupujících jednotlivé země
|
|
Československo na LOH 1972
Fotogalerie

Odkazy
Externí odkazy
 Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu Letní olympijské hry 1972 na Wikimedia Commons
Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu Letní olympijské hry 1972 na Wikimedia Commons - Oficiální výsledky LOH 1972 na Olympedia[nedostupný zdroj] (anglicky)
Média použitá na této stránce
(c) I, Cmapm, CC BY-SA 3.0
The flag of the Soviet Union (1955-1991) using a darker shade of red.
(c) I, Cmapm, CC BY-SA 3.0
The flag of the Soviet Union (1955-1991) using a darker shade of red.

Variant version of a flag of Japan, used between January 27, 1870 and August 13, 1999 (aspect ratio 7:10).
Flag of Second Polish Republic and later People's Republic of Poland in period from March 29, 1928 to March 10, 1980. Red shade used here is HTML "vermilion" #E34234. Proportion 5:8.
Autor: Scroch, Licence: CC BY-SA 3.0
Flag of Bulgaria (1971-1990). Flag of Bulgaria with Bulgarian coat from 1971.
Autor: Scroch, Licence: CC BY-SA 3.0
Flag of Bulgaria (1971-1990). Flag of Bulgaria with Bulgarian coat from 1971.
Finská vlajka
Vlajka České republiky. Podoba státní vlajky České republiky je definována zákonem České národní rady č. 3/1993 Sb., o státních symbolech České republiky, přijatým 17. prosince 1992 a který nabyl účinnosti 1. ledna 1993, kdy rozdělením České a Slovenské Federativní republiky vznikla samostatná Česká republika. Vlajka je popsána v § 4 takto: „Státní vlajka České republiky se skládá z horního pruhu bílého a dolního pruhu červeného, mezi něž je vsunut žerďový modrý klín do poloviny délky vlajky. Poměr šířky k její délce je 2 : 3.“
Vlajka České republiky. Podoba státní vlajky České republiky je definována zákonem České národní rady č. 3/1993 Sb., o státních symbolech České republiky, přijatým 17. prosince 1992 a který nabyl účinnosti 1. ledna 1993, kdy rozdělením České a Slovenské Federativní republiky vznikla samostatná Česká republika. Vlajka je popsána v § 4 takto: „Státní vlajka České republiky se skládá z horního pruhu bílého a dolního pruhu červeného, mezi něž je vsunut žerďový modrý klín do poloviny délky vlajky. Poměr šířky k její délce je 2 : 3.“
Flag of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1946-1992).
The design (blazon) is defined in Article 4 of the Constitution for the Republic of Yugoslavia (1946). [1]
The civil ensign and flag of Belgium. It is identical to Image:Flag of Belgium.svg except that it has a 2:3 ratio, instead of 13:15.
Flag of Jamaica. “The sunshine, the land is green, and the people are strong and bold” is the symbolism of the colours of the flag. GOLD represents the natural wealth and beauty of sunlight; GREEN represents hope and agricultural resources; BLACK represents the strength and creativity of the people. The original symbolism, however, was "Hardships there are, but the land is green, and the sun shineth", where BLACK represented the hardships being faced.
| Flag of Bolivia* | |
|---|---|
| country | Template:I18n/Republic of Bolivia |
| used by | Bolivia |
| from | 1851 |
| until | Present |
| created by | Government of Bolivia |
| format | 15:22 |
| shape | rectangular |
| colours | červená, žlutá, zelená
flag has 3 horizontal stripes |
| other characteristics | A horizontal tricolor of red, yellow and green. |
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
The Egyptian flag (1972-1984). Also the flag of Libya (1972-1977) and Syria (1972-1980), when the three countries formed the nominal “Federation of Arab Republics”. (For a map of the federation, see Image:Esl.PNG.)
The Arab text in the scroll held by the “Golden Hawk of Qureish” reads Arabic اتحاد الجمهوريات العربية, ittiħād al-jumhūriyyāt al-`arabiyya, i.e. the Federation (literally “Union”) of Arab Republics — in a quasi-Kufic script (in its original form, with a very ornamental letter dal د).
Made by author of Xramp, first uploaded by Denelson83 as Flag of Ecuador.svg, modifications by Husunqu.
The flag of Guam, courtesy an e-mail from the author of xrmap. Modifications by Denelson83.
Při zobrazení tohoto souboru lze snadno přidat orámování
Zelený pruh má znázorňovat většinové katolické obyvatelsto Irska, oranžový pruh reprezentuje protestantskou menšinu a bílý pruh uprostřed znázorňuje mír a harmonii mezi nimi.
The Flag of Iceland.
- Horizontal aspect ratio: 7:1:2:1:14;
- Vertical aspect ratio: 7:1:2:1:7.
Flag of the Ivory Coast, written by Jon Harald Søby, modified by Zscout370. The colors match to what is reported at http://fotw.vexillum.com/flags/ci.html.
Flag of the Ivory Coast, written by Jon Harald Søby, modified by Zscout370. The colors match to what is reported at http://fotw.vexillum.com/flags/ci.html.
Flag of Portugal, created by Columbano Bordalo Pinheiro (1857–1929), officially adopted by Portuguese government in June 30th 1911 (in use since about November 1910). Color shades matching the RGB values officially reccomended here. (PMS values should be used for direct ink or textile; CMYK for 4-color offset printing on paper; this is an image for screen display, RGB should be used.)
The flag of San Marino, before the 2011 standardization
Flag of Senegal
Used color: National flag | South African Government and Pantone Color Picker
| zelená | rendered as RGB 0 119 73 | Pantone 3415 C |
| žlutá | rendered as RGB 255 184 28 | Pantone 1235 C |
| červená | rendered as RGB 224 60 49 | Pantone 179 C |
| modrá | rendered as RGB 0 20 137 | Pantone Reflex Blue C |
| bílá | rendered as RGB 255 255 255 | |
| černá | rendered as RGB 0 0 0 |
The national flag of Kingdom of Thailand; there are total of 3 colours:
- Red represents the blood spilt to protect Thailand’s independence and often more simply described as representing the nation.
- White represents the religion of Buddhism, the predominant religion of the nation
- Blue represents the monarchy of the nation, which is recognised as the centre of Thai hearts.
State Flag of Venezuela 1930-2006, New flag was introduced 9 March 2006.
Autor: SanchoPanzaXXI, Licence: CC BY-SA 4.0
Flag of Spain during the Spanish State. It was adopted on 11 October 1945 with Reglamento de Banderas Insignias y Distintivos (Flags, Ensigns and Coats of Arms Bill)
Flag of Tunisia until 1999.
Flag of Liechtenstein 1937—1982.
The flag of the Ethiopian Empire with the Lion of Judah in the center
(c) Zscout370 na projektu Wikipedie v jazyce angličtina, CC BY-SA 3.0
The first flag of the nation of Lesotho, used from 1966 until 1987. Elements from this flag can be seen on the current national flag, in use starting in 2006.
Logo der XX. Olympischen Sommerspiele München 1972 (offizielle Farben)
Flag of Zambia before 1996
Flag of Romania, (21 August 1965 - 22 December 1989/officialy 27 December 1989).

Construction sheet of the Flag of Romania as depicted in Decree nr. 972 from 5 November 1968.
- l = 2/3 × L
- C = 1/3 × L
- S = 2/5 × l
Flag of the People's Republic of Congo between 1 January 1970 - 10 June 1991
The flag of Brazil from 1968 to 1992 with 23 stars.
Flag of Syria (1972-1980), while the country was in the Federation of Arab Republics. The Arab text in the scroll held by the “Golden Hawk of Qureish” reads Arabic اتحاد الجمهوريات العربية, ittiħād al-jumhūriyyāt al-`arabiyya, i.e. the Federation (literally “Union”) of Arab Republics — in a quasi-Kufic script (in its original form, with a very ornamental letter dal د). Unlike Libya and Egypt, Syria did not display its name on the flag during this period.
Flag of People's Republic of Mongolia 1945-1992
Flag of South Korea (1949-1984)
Flag of Suriname, constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands (1954-1974), from its adoption in 1959 until the achievement of independence on 25 November 1975, on which date the flag was changed to its current form.
Flag of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1946-1992).
The design (blazon) is defined in Article 4 of the Constitution for the Republic of Yugoslavia (1946). [1]
Autor:
3 by 2 pixels. Basically invisible. Useful if you want a gap with 3:2 ratio. Just write Blank.svg|Horizontal length in px, of course. This is just a vector version of the Blank.png, which was listed as the #1 candidate to be converted to SVG.
The Egyptian flag (1972-1984). Also the flag of Libya (1972-1977) and Syria (1972-1980), when the three countries formed the nominal “Federation of Arab Republics”. (For a map of the federation, see Image:Esl.PNG.)
The Arab text in the scroll held by the “Golden Hawk of Qureish” reads Arabic اتحاد الجمهوريات العربية, ittiħād al-jumhūriyyāt al-`arabiyya, i.e. the Federation (literally “Union”) of Arab Republics — in a quasi-Kufic script (in its original form, with a very ornamental letter dal د).
Autor: Tcfc2349, Licence: CC BY-SA 4.0
Flag of the Bahamas (1964-1973)
(c) Diego Delso, CC BY-SA 3.0
Olympiastadion, Munich, Germany
The flag of Afghanistan between 1931 and 1973 (1311–1352 A.P., 1351–1393 A.H.).
Flag of Cameroon, 1961-75
The flag of San Marino, before the 2011 standardization
Flag of Greece (1970–1975), adopted by the Greek military Junta; Aspect ratio: 7:12
The Saudi Arabian flag from 1938 to 1973.
1910 Flag of Bermuda (with smaller coat of arms)