Mare Imbrium

Mare Imbrium (česky Moře dešťů) je po oblasti Oceanus Procellarum druhé největší měsíční moře a současně největší měsíční kotlina.[1] Jedná se tak vlastně o jeden z největších známých impaktních kráterů ve Sluneční soustavě.[2]
Charakteristika
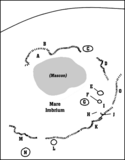
Rozkládá se na přivrácené straně Měsíce. Má přibližně kruhový tvar s průměrem 1 160 km[1] a je pozůstatkem po obřím impaktu před asi 3,9 miliardy roků.[3] Při impaktu vznikla pánev Imbrium, kterou obklopují nejméně dva soustředné prstence valů s průměrem 670 a 1160 km.[4] Impaktní pánev později vyplnila čedičová láva, čímž vzniklo samotné Moře dešťů. Mare Imbrium se nachází severovýchodně od středu měsíčního disku, jeho selenografické souřadnice středu jsou 34,7° S, 14,9° Z.[5] Jeho plocha je cca 830 000 km².[1] V této oblasti se nachází jeden z měsíčních masconů.
Centrální a severní část moře je chudá na větší krátery, zato ve východní části leží poblíž sebe trojice výrazných kráterů Autolycus, Archimedes a Aristillus. Na severním okraji lze nalézt velký tmavý kráter Plato. Obvod Mare Imbrium tvoří pohoří Montes Carpatus (na jihu), Montes Apenninus (jihovýchod), Montes Caucasus (východ), Montes Alpes (severovýchod). Na jihozápadě hraničí Mare Imbrium s Oceánem bouří (Oceanus Procellarum). Severozápadní část vyplňuje Sinus Iridum (Záliv duhy). Trosky vnitřního valu kotliny tvoří pohoří Montes Teneriffe, Montes Recti, Montes Spitzbergen a hora Mons Pico.
Expedice
Do oblasti Mare Imbrium poblíž kráteru Autolycus dopadla 13. září 1959 sovětská kosmická sonda Luna 2 (první sonda vyrobená člověkem, která dosáhla povrchu Měsíce)[6] a na okraji Mare Imbrium na úpatí měsíčního pohoří Montes Apenninus (Apeniny) v blízkosti brázdy Rima Hadley 30. července 1971 přistála americká expedice Apollo 15.[7] V sobotu 14. prosince 2013 přistál v severozápadní části Mare Imbrium jižně od kráteru Laplace F na souřadnicích 19,51° S, 44,12° Z čínský modul mise Čchang-e s vozítkem Nefritový králík.[8][9]
Mare Imbrium v kultuře
- Moře dešťů je zmíněno ve vědeckofantastických románech britského spisovatele Arthura C. Clarka Měsíční prach [10] a 3001: Poslední vesmírná odysea.
| Povrchové útvary v oblasti Mare Imbrium: A – Sinus Iridum (Záliv duhy) |
Odkazy
Reference
- ↑ a b c RÜKL, Antonín. Atlas Měsíce. Praha: Aventinum, 1991. ISBN 80-85277-10-7. Kapitola le Verrier, s. 48/11.
- ↑ https://www.stoplusjednicka.cz/svedkove-davnych-kolizi-nejvetsi-kratery-slunecni-soustavy
- ↑ MERLE, R. E.; NEMCHIN, A. A.; GRANGE, M. L. High resolution U-Pb ages of Ca-phosphates in Apollo 14 breccias: Implications for the age of the Imbrium impact. M&PS. 2014-12, roč. 49, čís. 12, s. 2241–2251. Dostupné online [cit. 2020-04-19]. ISSN 1086-9379. DOI:10.1111/maps.12395. (anglicky)
- ↑ GABZDYL, Pavel. Měsíc. Praha: Aventinum, 2006. ISBN 80-86858-22-7. S. Kapitola třetí, s. 152.
- ↑ Moon: Mare Imbrium, Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature, IAU, USGS, NASA (anglicky)
- ↑ RÜKL, Antonín. Atlas Měsíce. Praha: Aventinum, 1991. ISBN 80-85277-10-7. Kapitola Aristillus, s. 50/12.
- ↑ RÜKL, Antonín. Atlas Měsíce. Praha: Aventinum, 1991. ISBN 80-85277-10-7. Kapitola Conon, s. 70/22.
- ↑ China's Chang'e-3 probe and rover makes first moon landing in 37 years, collectspace.com, citováno 17. 12. 2013 (anglicky)
- ↑ Souřadnice místa přistání přistávacího modulu, China News, citováno 16. 12. 2013 (anglicky)
- ↑ CLARKE, Arthur Charles. Měsíční prach. Praha: Odeon, 1989. ISBN 80-207-0240-7. Kapitola třetí, s. 23.
Literatura
- RÜKL, Antonín. Atlas Měsíce. Praha: Aventinum, 1991. ISBN 80-85277-10-7.
Související články
Externí odkazy
 Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu Mare Imbrium na Wikimedia Commons
Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu Mare Imbrium na Wikimedia Commons
Média použitá na této stránce
Original description: Southward looking oblique view of Mare Imbrium and Copernicus crater on the Moon. Copernicus crater is seen almost edge-on near the horizon at the center. The crater is 107 km in diameter and is centered at 9.7 N, 20.1 W. In the foreground is Mare Imbrium, peppered with secondary crater chains and elongated craters due to the Copernicus impact. The large crater near the center of the image is the 20 km diameter Pytheas, at 20.5 N, 20.6 W. At the upper edge of the Mare Imbrium are the Montes Carpatus. The distance from the lower edge of the frame to the center of Copernicus is about 400 km. This picture was taken by the metric camera on Apollo 17. (Apollo 17, AS-2444).
Location & Time Information Date/Time (UT): 1972-12 Distance/Range (km): 160. Central Latitude/Longitude (deg): +20.,338. E Orbit(s): N/A
Imaging Information Area or Feature Type: crater, mare, crater chains Instrument: Metric Mapping camera Instrument Resolution (pixels): Film Type - 3400 Instrument Field of View (deg): 76.2 mm Focal Length Filter: None Illumination Incidence Angle (deg): 77. Phase Angle (deg): N/A Instrument Look Direction: N/A Surface Emission Angle (deg): 40.
Ordering Information CD-ROM Volume: N/A NASA Image ID number: AS17-2444 Other Image ID number: N/A NSSDC Data Set ID (Photo): 72-096A-03A NSSDC Data Set ID (CD): N/AOther ID: N/A
Autor: Srbauer, Licence: CC BY-SA 3.0
A map of Mare Imbrium.
- A: Sinus Iridum (Regenbogenbucht)
- B: Montes Jura (Jura-Gebirge)
- C: Plato
- D: Montes Alpes (Alpen)
- E: Aristillus
- F: Autolycus
- G: Archimedes
- H: Palus Putretinis (Sumpf der Fäulnis)
- I: Hadley Rille
- J: Apollo 15 landing site
- K: Montes Apenninus (Apenninen)
- L: Erathostenes
- M: Montes Carpatus (Karpaten)
- N: Copernicus
- O: Montes Caucasus (Kaukasus)
Mare Imbrium sits in the Imbrium basin. The basin material is of the Lower Imbrian epoch, with the mare material being of the Upper Imbrian and Eratosthenian epochs. The mare is lined with mountian ranges called montes to the south. The crater Copernicus is just visible in the bottom of the photo, while Plato is clearly seen on the northern rim. Sinus Iridum is seen connected to the mare on the northwestern rim. The crater Archimedes also visible in the picture as the lighter circular feature in the southeastern region of the mare.
Autor: M. Gålfalk, G. Olofsson, and H.-G. Florén; SIRCA camera, Licence: CC BY-SA 3.0
Sea of Rains, on the en:Moon. Infrared image in L band centred on 3.75 micrometres. Taken with the SIRCA camera by M. Gålfalk, G. Olofsson, and H.-G. Florén. Nordic Optical Telescope, Stockholm Observatory. More images can be found here.