SN 1054
SN 1054 nebo Supernova 1054 byla supernova poprvé pozorovaná ze Země 4. července 1054. Zaznamenali ji čínští a arabští astronomové, kteří uvádějí, že byla viditelná přes den 23 dní a v noci 653 dní. Pravděpodobně to byla supernova typu II. Na místě supernovy SN 1054 se dnes nachází Krabí mlhovina. Krabí mlhovina má také označení Messier 1, jako první objekt, který do svého katalogu zaznamenal francouzský astronom Charles Messier v roce 1774. V roce 1963 se z oblasti mlhoviny podařilo detekovat rentgenové záření. Jeho zdrojem je objekt s názvem Taurus X-1. Energie, kterou vyzařuje mlhovina v rentgenovém spektru je 100krát vyšší než energie vyzařována ve viditelné části spektra. V centru mlhoviny byl objeven 9. listopadu 1968 pomocí 300metrové antény v observatoři Arecibo (Portoriko) pulzující rádiový zdroj nazvaný Krabí pulsar. Kolem své osy se otočí 30krát za sekundu.
Historie pozorování
Tento vesmírný úkaz zřejmě pozorovali arabští (Ibn Butlán) i čínští astronomové. V Severní Americe možná příslušníci indiánského kmene Hopiů (jak dokládají objevené skalní kresby z této doby).[1] Americké kresby ale mohou reprezentovat jiné úkazy (Halleyova kometa).
Reference
Externí odkazy
 Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu SN 1054 na Wikimedia Commons
Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu SN 1054 na Wikimedia Commons
Média použitá na této stránce
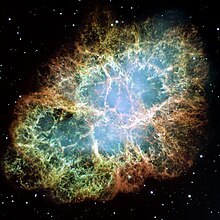
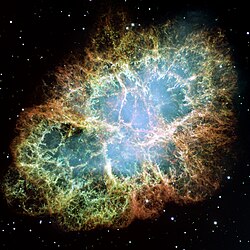
This is a mosaic image, one of the largest ever taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, of the Crab Nebula, a six-light-year-wide expanding remnant of a star's supernova explosion. Japanese and Chinese astronomers recorded this violent event in 1054 CE.
The orange filaments are the tattered remains of the star and consist mostly of hydrogen. The rapidly spinning neutron star embedded in the center of the nebula is the dynamo powering the nebula's eerie interior bluish glow. The blue light comes from electrons whirling at nearly the speed of light around magnetic field lines from the neutron star. The neutron star, like a lighthouse, ejects twin beams of radiation that appear to pulse 30 times a second due to the neutron star's rotation. A neutron star is the crushed ultra-dense core of the exploded star.
The Crab Nebula derived its name from its appearance in a drawing made by Irish astronomer Lord Rosse in 1844, using a 36-inch telescope. When viewed by Hubble, as well as by large ground-based telescopes such as the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope, the Crab Nebula takes on a more detailed appearance that yields clues into the spectacular demise of a star, 6,500 light-years away.
The newly composed image was assembled from 24 individual Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 exposures taken in October 1999, January 2000, and December 2000. The colors in the image indicate the different elements that were expelled during the explosion. Blue in the filaments in the outer part of the nebula represents neutral oxygen, green is singly-ionized sulfur, and red indicates doubly-ionized oxygen.