Seznam největších ostrovů




Tento seznam řadí ostrovy světa podle jejich rozlohy. Obsahuje 50 plošně největších ostrovů světa, tedy všechny ostrovy s rozlohou nad 18 500 km². Pro porovnání jsou níže uvedeny i kontinentální masy kontinentů.
Ostrovy
| Pořadí | Jméno | Rozloha (km²) | Kontinent | Stát(y) | Poznámka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Grónsko | 2 130 750[1] | Severní Amerika | ||
| 2. | Nová Guinea | 785 753 | Oceánie |
| |
| 3. | Borneo | 748 168 | Asie | ostrov rozdělený mezi nejvíce suverénních států (3) | |
| 4. | Madagaskar | 587 041[1] | Afrika | ||
| 5. | Baffinův ostrov | 507 451[2] | Severní Amerika | ||
| 6. | Sumatra | 443 066 | Asie | ||
| 7. | Honšú | 225 800 | Asie | ||
| 8. | Viktoriin ostrov | 217 291[2] | Severní Amerika | ||
| 9. | Velká Británie | 216 325[3] | Evropa | ||
| 10. | Ellesmerův ostrov | 196 236[2] | Severní Amerika | ||
| 11. | Sulawesi (Celebes) | 180 681 | Asie | ||
| 12. | Jižní ostrov (Nový Zéland) | 145 836 | Oceánie | ||
| 13. | Jáva | 138 794 | Asie | nejlidnatější ostrov světa | |
| 14. | Severní ostrov (Nový Zéland) | 111 583 | Oceánie | ||
| 15. | Luzon | 109 965 | Asie | ||
| 16. | Newfoundland | 108 860[2] | Severní Amerika | ||
| 17. | Kuba (hlavní ostrov) | 105 806 | Severní Amerika | největší ostrov Střední i Latinské Ameriky | |
| 18. | Island (hlavní ostrov) | 101 826 | Evropa | ||
| 19. | Mindanao | 97 530 | Asie | ||
| 20. | Irsko | 81 638 | Evropa | ||
| 21. | Hokkaidó | 78 719 | Asie | ||
| 22. | Hispaniola | 73 929 | Severní Amerika |
| |
| 23. | Sachalin | 72 493 | Asie | ||
| 24. | Banksův ostrov | 70 028[2] | Severní Amerika | ||
| 25. | Cejlon | 65 268[1] | Asie | ||
| 26. | Tasmánie | 64 519[4] | Oceánie | ||
| 27. | Devon | 55 247[2] | Severní Amerika | ||
| 28. | Ostrov Alexandra I. | 49 070 | Antarktida | Antarktida | největší trvale neobydlený ostrov světa |
| 29. | Ohňová země | 47 401 | Jižní Amerika | ||
| 30. | Severní ostrov Nové země | 47 079 | Evropa | ||
| 31. | Berknerův ostrov | 43 873 | Antarktida | Antarktida | |
| 32. | ostrov Axela Heiberga | 43 178 | Severní Amerika | ||
| 33. | Melvillův ostrov | 42 149 | Severní Amerika | ||
| 34. | Southampton | 41 214 | Severní Amerika | ||
| 35. | Marajó | 40 100 | Jižní Amerika | největší říční (resp. deltový) ostrov světa | |
| 36. | Západní Špicberk | 38 981 | Evropa | Špicberky pod správou | |
| 37. | Kjúšú | 37 437 | Asie | ||
| 38. | Nová Británie | 35 145 | Oceánie | ||
| 39. | Tchaj-wan | 32 260 | Asie | nárokovaný Čínskou lidovou republikou | |
| 40. | Ostrov prince Waleského | 33 339 | Severní Amerika | ||
| 41. | Jižní ostrov Nové země | 33 246 | Evropa | ||
| 42. | Chaj-nan | 33 210 | Asie | ||
| 43. | Vancouver | 32 134 | Severní Amerika | ||
| 44. | Timor | 28 418 | Asie | ||
| 45. | Sicílie | 25 662 | Evropa | ||
| 46. | Somerset | 24 786 | Severní Amerika | ||
| 47. | Sardinie | 23 949 | Evropa | ||
| 48. | Kotěľnyj | 23 165 | Asie | ||
| 49. | Bananal | 20 000 | Jižní Amerika | vnitrozemský říční ostrov, největší ostrov obklopený pouze sladkou vodou | |
| 50. | Šikoku | 18 545 | Asie |
Kontinentální masy kontinentů
Níže uvedené rozlohy zahrnují pouze samotné kontinenty bez přilehlých ostrovů.
| Pořadí | Jméno | Rozloha (km²) | státy | poznámka |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Eurafrasie | 79 810 726 | 126 suverénních států a další území |
|
| 2. | Amerika | 37 699 623 | 22 států a 1 závislé území | |
| 3. | Antarktida | 12 272 800 | 0 (7 neuplatňovaných územních nároků) | rozloha bez šelfových ledovců |
| 4. | Austrálie | 7 591 608 |
Antarktida by bez příkrovu pevninského ledovce nebyla souvislou kontinentální masou, ale obrovským souostrovím.[5] Bez zatížení ledovcem by však zároveň došlo k jejímu vyzdvižení, takže rozsah souše by byl větší než při prostém odečtení ledového pokryvu.
Rozloha nejmenšího kontinentu (Austrálie) je řádově v podobném poměru k největšímu ostrovu (Grónsko), jako je Grónsko k druhému největšímu ostrovu (Nová Guinea). Oproti Grónsku má však Austrálie z geologického hlediska jednoznačně charakter samostatného kontinentu.
Reference
- ↑ a b c Joshua Calder's World Island Info
- ↑ a b c d e f Atlas Kanady. atlas.nrcan.gc.ca [online]. [cit. 2007-06-27]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném dne 2013-01-22.
- ↑ Velký atlas světa. Praha: Kartografie Praha, a. s., 1993. ISBN 80-7011-265-4.
- ↑ Australian Government Geoscience Australia. www.ga.gov.au [online]. [cit. 2007-07-02]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném dne 2008-07-30.
- ↑ Global warming and the stability of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, Michael Oppenheimer, 1998
Související články
Média použitá na této stránce
bendera Indonesia
Flag of Canada introduced in 1965, using Pantone colors. This design replaced the Canadian Red Ensign design.
The Flag of Iceland.
- Horizontal aspect ratio: 7:1:2:1:14;
- Vertical aspect ratio: 7:1:2:1:7.
Zelený pruh má znázorňovat většinové katolické obyvatelsto Irska, oranžový pruh reprezentuje protestantskou menšinu a bílý pruh uprostřed znázorňuje mír a harmonii mezi nimi.
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
The national and official state flag of Haiti; arms obtained from File:Coat of arms of Haiti.svg. The civil flag can be found at here.
Flag of Australia, when congruence with this colour chart is required (i.e. when a "less bright" version is needed).
See Flag of Australia.svg for main file information.Při zobrazení tohoto souboru lze snadno přidat orámování
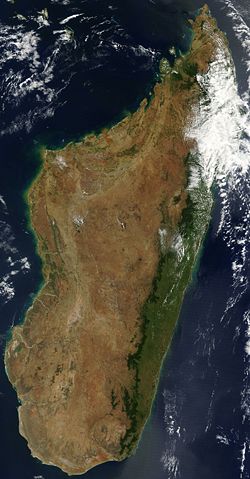
Satellite image of Madagascar in September 2003. Slightly cropped, original taken from NASA's Visible Earth: [1]. Original description:
- The world's fourth largest island, Madagascar, is featured in this Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) image taken by the Terra satellite on September 10, 2003. Several active fires, marked with red dots, burn in the central highlands, which are primarily covered with rice fields. The fires are probably controlled burns to clear farmland. The narrow strip of green along the east coast of the island is a rain forest. The west coast is lined with baobabs, a desert tree with a fat trunk, and thorny forest.
Satellite picture of New Guinea
Satellite photo highlighting the island of Greenland, as well as Iceland and the Canadian Arctic Archipelago.