Seznam států světa podle indexu lidského rozvoje
Toto je seznam států světa podle indexu lidského rozvoje tak, jak jej vydává Organizace spojených národů prostřednictvím rozvojového programu OSN ve výroční zprávě o programu rozvoje.[2] Zpráva o lidském rozvoji je publikována OSN každoročně, až na výjimky, od roku 1990. Zpráva z roku 2019 založená na datech z roku 2018 obsahuje HDI 189 zemí a 15 regionů nebo skupin na základě údajů shromážděných v roce 2018.
Index lidského rozvoje (HDI) je komparativní nástroj k poměření kvality lidského života, za pomoci porovnání údajů o chudobě, gramotnosti, vzdělání, střední délky života, porodnosti a dalších faktorů. Index rozlišuje zda je země rozvinutá (vyspělá), rozvojová nebo nejméně rozvinutá a rovněž poměřuje vliv ekonomických politik na kvalitu života. Index vymyslel v roce 1990 pákistánský ekonom Mahbub al Hak.[3]
Index lidského rozvoje rozděluje státy do čtyř skupin na základě jejich HDI, a to na země, jejichž HDI velmi vysoký, vysoký, střední nebo nízký.
Kompletní seznam států
- ▲ = růst
- ▬ = stálost
- ▼ = pokles
Velmi vysoký
| Pořadí | Stát | HDI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data z roku 2021 (ze zprávy za rok 2022) [2] | Změna oproti roku 2015 | Data z roku 2021 (ze zprávy za rok 2021) [2] | Průměrný roční růst [2] | |
| 1 | ▬ | 0,962 | ▲ 0,19% | |
| 2 | ▬ | 0,961 | ▲ 0,19% | |
| 3 | ▬ | 0,959 | ▲ 0,56% | |
| 4 | ▲ (3) | 0,952 | ▲ 0,44% | |
| 5 | ▲ (3) | 0,951 | ▲ 0,27% | |
| 6 | ▬ | 0,948 | ▲ 0,34% | |
| 7 | ▼ (2) | 0,947 | ▲ 0,36% | |
| 8 | ▲ (6) | 0,945 | ▲ 0,40% | |
| 9 | ▼ (5) | 0,942 | ▲ 0,16% | |
| 10 | ▼ (1) | 0,941 | ▲ 0,24% | |
| 11 | ▬ | 0,940 | ▲ 0,29% | |
| 12 | ▼ (1) | 0,939 | ▲ 0,29% | |
| 13 | ▲ (2) | 0,937 | ▲ 0,25% | |
| 13 | ▼ (3) | 0,937 | ▲ 0,15% | |
| 15 | ▼ (2) | 0,936 | ▲ 0,25% | |
| 16 | ▼ (1) | 0,935 | ▲ 0,22% | |
| 17 | ▲ (3) | 0,930 | ▲ 0,18% | |
| 18 | ▼ (3) | 0.929 | ▲ 0,17% | |
| 19 | ▬ | 0,925 | ▲ 0,27% | |
| 19 | ▲ (3) | 0,925 | ▲ 0,35% | |
| 21 | ▼ (3) | 0,921 | ▲ 0,10% | |
| 22 | ▬ | 0,919 | ▲ 0,25% | |
| 23 | ▲ (4) | 0,918 | ▲ 0,58% | |
| 23 | ▲ (1) | 0,918 | ▲ 0,28% | |
| 25 | ▼ (3) | 0,916 | ▲ 0,14% | |
| 26 | ▲ (9) | 0,911 | ▲ 0,80% | |
| 27 | ▬ | 0,905 | ▲ 0,38% | |
| 28 | ▼ (3) | 0,903 | ▲ 0,27% | |
| 29 | ▲ (3) | 0,896 | ▲ 0,41% | |
| 30 | ▼ (1) | 0,895 | ▲ 0,13% | |
| 31 | ▼ (2) | 0,890 | ▲ 0,30% | |
| 32 | ▼ (6) | 0,889 | ▲ 0,20% | |
| 33 | ▼ (2) | 0,887 | ▲ 0,19% | |
| 34 | ▼ (1) | 0,876 | ▲ 0,37% | |
| 35 | ▲ (3) | 0,875 | ▲ 0,73% | |
| 35 | ▲ (1) | 0,875 | ▲ 0,35% | |
| 35 | ▲ (2) | 0,875 | ▲ 0,64% | |
| 38 | ▲ (2) | 0,866 | ▲ 0,40% | |
| 39 | ▲ (1) | 0,863 | ▲ 0,42% | |
| 40 | ▼ (6) | 0,858 | ▲ 0,11% | |
| 40 | ▲ (5) | 0,858 | ▲ 0,40% | |
| 42 | ▲ (1) | 0,855 | ▲ 0,46% | |
| 42 | ▲ (1) | 0,855 | ▲ 0,23% | |
| 44 | NA | 0,853 | NA | |
| 45 | ▼ (5) | 0,848 | ▲ 0,09% | |
| 46 | ▲ (1) | 0,846 | ▲ 0,20% | |
| 47 | ▼ (4) | 0,842 | ▲ 0,09% | |
| 48 | ▲ (6) | 0,838 | ▲ 1,03% | |
| 49 | ▲ (3) | 0,832 | ▲ 0,27% | |
| 50 | ▼ (1) | 0,831 | ▲ 0,20% | |
| 51 | ▼ (3) | 0,829 | ▲ 0,01% | |
| 52 | ▼ (2) | 0,822 | ▲ 0,29% | |
| 53 | ▼ (4) | 0,821 | ▲ 0,16% | |
| 54 | ▼ (3) | 0,816 | ▲ 0,32% | |
| 55 | ▼ (2) | 0,812 | ▬ 0.00% | |
| 56 | ▲ (4) | 0,811 | ▲ 0,51% | |
| 57 | ▼ (2) | 0,810 | ▲ 0,23% | |
| 58 | ▲ (4) | 0,809 | ▲ 0,43% | |
| 58 | ▬ | 0,809 | ▲ 0,25% | |
| 60 | ▼ (3) | 0,808 | ▲ 0,21% | |
| 61 | ▬ | 0,805 | ▲ 0,37% | |
| 62 | ▲ (1) | 0,803 | ▲ 0,39% | |
| 63 | ▲ (7) | 0,802 | ▲ 0,50% | |
| 63 | ▲ (2) | 0,802 | ▲ 0,55% | |
| 63 | ▲ (4) | 0,802 | ▲ 0,41% | |
| 66 | ▲ (6) | 0,800 | ▲ 0,75% | |
Vysoký
| Pořadí | Stát | HDI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data z roku 2021 (ze zprávy za rok 2022) [2] | Změna oproti roku 2015 | Data z roku 2021 (ze zprávy za rok 2022) [2] | Průměrný roční růst [2] | |
| 67 | ▼ (2) | 0.796 | ▲ 0.49% | |
| 68 | ▼ (9) | 0.795 | ▲ 0.06% | |
| 68 | ▲ (2) | 0.795 | ▲ 0.15% | |
| 70 | ▼ (2) | 0.790 | ▲ 0.02% | |
| 71 | ▼ (3) | 0.788 | ▼ 0.02% | |
| 72 | ▼ (8) | 0.785 | ▲ 0.10% | |
| 73 | ▲ (9) | 0.782 | ▲ 0.54% | |
| 74 | ▲ (10) | 0.780 | ▲ 0.67% | |
| 75 | ▲ (2) | 0.777 | ▲ 0.21% | |
| 76 | ▼ (2) | 0.774 | ▲ 0.35% | |
| 77 | ▼ (2) | 0.773 | ▲ 0.11% | |
| 78 | ▲ (5) | 0.762 | ▲ 0.39% | |
| 79 | ▲ (19) | 0.768 | ▲ 0.97% | |
| 80 | ▲ (16) | 0.767 | ▲ 0.73% | |
| 80 | ▲ (9) | 0.767 | ▲ 0.45% | |
| 80 | ▼ (7) | 0.767 | ▼ 0.07% | |
| 83 | ▼ (7) | 0.764 | ▼ 0.19% | |
| 84 | ▲ (1) | 0.762 | ▲ 0.45% | |
| 85 | ▼ (5) | 0.759 | ▲ 0.16% | |
| 86 | ▼ (8) | 0.758 | ▲ 0.15% | |
| 87 | ▲ (1) | 0.754 | ▲ 0.38% | |
| 88 | ▼ (1) | 0.752 | ▲ 0.32% | |
| 89 | ▼ (4) | 0.751 | ▲ 0.21% | |
| 90 | ▲ (6) | 0.747 | ▲ 0.75% | |
| 91 | ▲ (2) | 0.745 | ▲ 0.30% | |
| 91 | ▼ (1) | 0.745 | ▲ 0.22% | |
| 91 | ▲ (10) | 0.745 | ▲ 0.40% | |
| 91 | ▲ (2) | 0.745 | ▲ 0.43% | |
| 95 | ▼ (14) | 0.740 | ▲ 0.05% | |
| 96 | ▲ (4) | 0.739 | ▲ 0.48% | |
| 97 | ▲ (3) | 0.731 | ▲ 0.73% | |
| 97 | ▲ (1) | 0.731 | ▲ 0.14% | |
| 99 | ▲ (3) | 0.730 | ▲ 0.20% | |
| 99 | ▼ (7) | 0.730 | ▲ 0.09% | |
| 101 | ▲ (11) | 0.727 | ▲ 0.70% | |
| 102 | ▲ (11) | 0.720 | ▲ 0.11% | |
| 102 | ▲ (2) | 0.720 | ▼ 0.06% | |
| 104 | ▲ (10) | 0.718 | ▼ 0.26% | |
| 105 | ▼ (2) | 0.717 | ▲ 0.42% | |
| 106 | ▲ (2) | 0.715 | ▲ 0.36% | |
| 106 | ▼ (11) | 0.715 | ▼ 0.16% | |
| 108 | ▲ (12) | 0.714 | ▲ 0.77% | |
| 109 | ▼ (4) | 0.713 | ▲ 0.50% | |
| 110 | ▼ (3) | 0.709 | ▲ 0.06% | |
| 111 | ▼ (6) | 0.707 | ▼ 0.08% | |
| 112 | ▲ (2) | 0.706 | ▲ 0.56% | |
| 112 | ▼ (21) | 0.706 | ▼ 0.79% | |
| 114 | ▲ (3) | 0.705 | ▲ 0.55% | |
| 115 | ▲ (5) | 0.703 | ▲ 0.53% | |
Střední
| Pořadí | Stát | HDI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data z roku 2021 (ze zprávy za rok 2022) [2] | Změna oproti roku 2015 | Data z roku 2021 (ze zprávy za rok 2022) [2] | Průměrný roční růst [2] | |
| 116 | ▬ | 0.699 | ▲ 0.33% | |
| 117 | ▼ (6) | 0.693 | ▲ 0.44% | |
| 118 | ▬ | 0.692 | ▲ 0.40% | |
| 118 | ▬ | 0.692 | ▲ 0.38% | |
| 120 | ▼ (41) | 0.691 | ▼ 0.80% | |
| 121 | ▲ (1) | 0.686 | ▲ 0.63% | |
| 122 | ▲ (3) | 0.685 | ▲ 0.68% | |
| 123 | ▼ (14) | 0.683 | ▼ 0.31% | |
| 123 | ▲ (3) | 0.683 | ▲ 1.14% | |
| 125 | ▼ (2) | 0.675 | ▲ 0.22% | |
| 126 | ▲ (1) | 0.667 | ▲ 0.76% | |
| 127 | ▲ (6) | 0.666 | ▲ 1.25% | |
| 128 | ▼ (4) | 0.662 | ▲ 0.25% | |
| 129 | ▲ (11) | 0.661 | ▲ 1.64% | |
| 130 | ▼ (2) | 0.641 | ▲ 0.36% | |
| 131 | ▼ (1) | 0.639 | NA | |
| 132 | ▼ (1) | 0.633 | ▲ 0.88% | |
| 133 | ▲ (5) | 0.632 | ▲ 0.88% | |
| 134 | ▬ | 0.628 | ▲ 0.04% | |
| 135 | ▼ (6) | 0.627 | ▲ 0.33% | |
| 136 | ▼ (1) | 0.624 | ▲ 0.53% | |
| 137 | ▬ | 0.621 | ▲ 0.36% | |
| 138 | ▲ (4) | 0.618 | ▲ 1.00% | |
| 139 | ▼ (7) | 0.624 | ▲ 0.46% | |
| 140 | ▲ (1) | 0.607 | ▲ 0.88% | |
| 140 | ▼ (4) | 0.607 | ▼ 0.18% | |
| 140 | ▲ (3) | 0.607 | ▲ 0.24% | |
| 143 | ▲ (4) | 0.602 | ▲ 0.94% | |
| 144 | ▼ (4) | 0.597 | ▲ 1.57% | |
| 145 | ▼ (6) | 0.596 | ▲ 0.26% | |
| 146 | ▲ (3) | 0.593 | ▲ 0.85% | |
| 146 | ▼ (1) | 0.593 | ▲ 1.34% | |
| 148 | ▼ (3) | 0.586 | ▲ 1.27% | |
| 149 | ▲ (1) | 0.585 | ▲ 1.26% | |
| 150 | ▲ (5) | 0.577 | ▼ 1.21% | |
| 151 | ▲ (2) | 0.576 | ▲ 1.06% | |
| 152 | ▬ | 0.575 | ▲ 0.49% | |
| 153 | ▼ (9) | 0.571 | ▲ 0.16% | |
| 154 | ▼ (4) | 0.565 | ▲ 0.60% | |
| 155 | ▼ (1) | 0.564 | ▲ 0.23% | |
| 156 | ▬ | 0.558 | ▲ 0.64% | |
| 156 | ▲ (2) | 0.558 | ▲ 1.02% | |
| 158 | ▼ (2) | 0.556 | ▲ 0.79% | |
| 159 | ▲ (8) | 0.550 | ▲ 1.38% | |
Nízký
| Pořadí | Stát | HDI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Údaj za rok 2022 [2] | Změna oproti údajům z roku 2015 | Údaj za rok 2022 [2] | Průměrný roční růst [2] | |
| 160 | ▲ (2) | 0.549 | ▲ 0.98% | |
| 161 | ▼ (2) | 0.544 | ▲ 0.68% | |
| 162 | ▲ (4) | 0.539 | ▲ 1.12% | |
| 163 | ▼ (3) | 0.535 | ▲ 1.94% | |
| 163 | ▲ (1) | 0.535 | ▲ 0.95% | |
| 165 | ▬ | 0.534 | ▲ 0.80% | |
| 166 | ▼ (6) | 0.525 | ▲ 0.59% | |
| 166 | ▼ (3) | 0.525 | ▲ 0.41% | |
| 168 | ▲ (3) | 0.514 | ▲ 0.88% | |
| 169 | ▲ (4) | 0.512 | ▲ 1.06% | |
| 170 | ▼ (1) | 0.511 | ▲ 0.80% | |
| 171 | ▲ (1) | 0.509 | ▲ 0.96% | |
| 172 | ▼ (4) | 0.508 | ▲ 0.40% | |
| 173 | ▼ (3) | 0.501 | ▲ 0.16% | |
| 174 | ▲ (1) | 0.500 | ▲ 0.76% | |
| 175 | ▲ (6) | 0.498 | ▲ 1.74% | |
| 176 | ▼ (2) | 0.492 | ▲ 0.55% | |
| 177 | ▲ (2) | 0.483 | ▲ 0.79% | |
| 178 | ▬ | 0.481 | ▲ 0.41% | |
| 179 | ▲ (1) | 0.479 | ▲ 1.01% | |
| 180 | ▼ (5) | 0.478 | ▲ 0.59% | |
| 181 | ▲ (1) | 0.477 | ▲ 0.59% | |
| 182 | ▲ (1) | 0.465 | ▲ 1.04% | |
| 183 | ▼ (6) | 0.455 | ▼ 1.03% | |
| 184 | ▲ (2) | 0.449 | ▲ 1.72% | |
| 185 | ▼ (2) | 0.446 | ▲ 0.95% | |
| 186 | ▲ (1) | 0.428 | ▲ 0.53% | |
| 187 | ▼ (2) | 0.426 | ▲ 0.46% | |
| 188 | ▲ (2) | 0.404 | ▲ 0.75% | |
| 189 | ▲ (2) | 0.400 | ▲ 1.54% | |
| 190 | ▼ (1) | 0.394 | ▲ 1.54% | |
| 191 | ▼ (3) | 0.385 | ▼ 1.00% | |
Seznam státu podle kontinentů
Afrika
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Severní Amerika
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Jižní Amerika
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Asie
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Evropa
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Austrálie a Oceánie
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Seznam podle regionů
Evropská unie
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Liga arabských států
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Východní Asie a Tichomoří
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Latinská Amerika
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Blízký východ a Severní Afrika
10 nejvyšších HDI
| 10 nejnižších HDI
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
HDI podle regionů a skupin států
| Region / Skupina | HDI za rok 2014 (odhad z roku 2015)[2] | HDI za rok 2013 (odhad z roku 2014)[4] |
|---|---|---|
| Velmi vysoký | ||
| Země s velmi vysokým HDI | 0.890 | 0.905 |
| OECD | 0.874 | 0.887 |
| Vysoký | ||
| Latinská Amerika a Karibik | 0.740 | 0.741 |
| Evropa a Střední Asie | 0.738 | 0.771 |
| Země s vysokým HDI | 0.735 | 0.758 |
| Východní Asie a Tichomoří | 0.703 ▲ | 0.683 |
| Svět celkem | 0.702 ▲ | 0.694 |
| Střední | ||
| Arabský svět | 0.682 ▲ | 0.652 |
| Malé ostrovní rozvojové státy | 0.665 ▲ | 0.648 |
| Země se středním HDI | 0.614 | 0.640 |
| Jižní Asie | 0.588 ▲ | 0.558 |
| Nízký | ||
| Subsaharská Afrika | 0.502 ▲ | 0.475 |
| Země s nízkým HDI | 0.493 ▲ | 0.466 |
| Nejméně rozvinuté země | 0.487 ▲ | 0.449 |
Země chybějící v poslední zprávě o HDI
* spočítáno UNDP (Rozvojovým programem OSN)
Členové OSN (toto nejsou údaje UNDP)
| Země a území, které nejsou členy OSN (toto nejsou údaje UNDP)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Odkazy
Poznámky
- ↑ OSN nepočítá HDI pro Macau. Vláda této země si počítá HDI vlastní.[6]
- ↑ OSN neuznává Čínskou republiku (Tchaj-wan) jako suverénní stát. Vláda této země si proto počítá HDI vlastní.[7]
Reference
V tomto článku byl použit překlad textu z článku Human Development Index na anglické Wikipedii.
- ↑ UNDP (United Nations Development Programme). Human Development Report 2023-24: Breaking the gridlock: Reimagining cooperation in a polarized world [online]. New York: 2024. Kapitola Table 3, s. 283. Dostupné online. ISBN 9789213588703. (anglicky)
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Human Development Report 2021/2022 [online]. Rozvojový program OSN, 2022 [cit. 2023-12-15]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném z originálu dne 2022-09-08. (anglicky)
- ↑ History of the Human Development Report [online]. Rozvojový program OSN [cit. 2009-07-26]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném dne 2013-11-04. (anglicky)
- ↑ 2014 Human development Report [online]. Rozvojový program OSN, 2014-07-24 [cit. 2016-09-10]. Dostupné online. (anglicky)
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az AVAKOV, Alexander V. Quality of Life, Balance of Power, and Nuclear Weapons (2016) [online]. Algora Publishing, 2016-06-02. Dostupné online. (anglicky)
- ↑ Macao in Figures [online]. Government of Macao Special Administrative Region, 2016. Dostupné online. (anglicky)
- ↑ 人類發展指數 / Human Development Index [online]. Directorate General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics, Executive Yuan, R.O.C., 2016 [cit. 2016-09-11]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném dne 2017-08-11. (čínsky)
- ↑ About Kosovo [online]. Rozvojový program OSN, 2015 [cit. 2016-09-11]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném dne 2019-01-26. (anglicky)
Související články
Externí odkazy
- (anglicky) Reports Archivováno 17. 12. 2020 na Wayback Machine. – Rozvojový program OSN – Zprávy o lidském rozvoji
Média použitá na této stránce
The Flag of Iceland.
- Horizontal aspect ratio: 7:1:2:1:14;
- Vertical aspect ratio: 7:1:2:1:7.
Flag of Australia, when congruence with this colour chart is required (i.e. when a "less bright" version is needed).
See Flag of Australia.svg for main file information.Zelený pruh má znázorňovat většinové katolické obyvatelsto Irska, oranžový pruh reprezentuje protestantskou menšinu a bílý pruh uprostřed znázorňuje mír a harmonii mezi nimi.
Finská vlajka
This is the national flag of Belgium, according to the Official Guide to Belgian Protocol. It has a 13:15 aspect ratio, though it is rarely seen in this ratio.
Its colours are defined as Pantone black, Pantone yellow 115, and Pantone red 032; also given as CMYK 0,0,0,100; 0,8.5,79,0; and 0,94,87,0.Flag of Canada introduced in 1965, using Pantone colors. This design replaced the Canadian Red Ensign design.
Flag of Liechtenstein
Vlajka České republiky. Podoba státní vlajky České republiky je definována zákonem České národní rady č. 3/1993 Sb., o státních symbolech České republiky, přijatým 17. prosince 1992 a který nabyl účinnosti 1. ledna 1993, kdy rozdělením České a Slovenské Federativní republiky vznikla samostatná Česká republika. Vlajka je popsána v § 4 takto: „Státní vlajka České republiky se skládá z horního pruhu bílého a dolního pruhu červeného, mezi něž je vsunut žerďový modrý klín do poloviny délky vlajky. Poměr šířky k její délce je 2 : 3.“
Flag of Portugal, created by Columbano Bordalo Pinheiro (1857-1929), officially adopted by Portuguese government in June 30th 1911 (in use since about November 1910).
Při zobrazení tohoto souboru lze snadno přidat orámování
Při zobrazení tohoto souboru lze snadno přidat orámování
Georgian flag in Pantone MS.
The national flag of Kingdom of Thailand; there are total of 3 colours:
- Red represents the blood spilt to protect Thailand’s independence and often more simply described as representing the nation.
- White represents the religion of Buddhism, the predominant religion of the nation
- Blue represents the monarchy of the nation, which is recognised as the centre of Thai hearts.
Flag of Iran. The tricolor flag was introduced in 1906, but after the Islamic Revolution of 1979 the Arabic words 'Allahu akbar' ('God is great'), written in the Kufic script of the Qur'an and repeated 22 times, were added to the red and green strips where they border the white central strip and in the middle is the emblem of Iran (which is a stylized Persian alphabet of the Arabic word Allah ("God")).
The official ISIRI standard (translation at FotW) gives two slightly different methods of construction for the flag: a compass-and-straightedge construction used for File:Flag of Iran (official).svg, and a "simplified" construction sheet with rational numbers used for this file.
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
The flag of the Dominican Republic has a centered white cross that extends to the edges. This emblem is similar to the flag design and shows a bible, a cross of gold and 6 Dominican flags. There are branches of olive and palm around the shield and above on the ribbon is the motto "Dios,Patria!, Libertad" ("God, Country, Freedom") and to amiable freedom. The blue is said to stand for liberty, red for the fire and blood of the independence struggle and the white cross symbolized that God has not forgotten his people. "Republica Dominicana". The Dominican flag was designed by Juan Pablo Duarte, father of the national Independence of Dominican Republic. The first dominican flag was sewn by a young lady named Concepción Bona, who lived across the street of El Baluarte, monument where the patriots gathered to fight for the independence, the night of February 27th, 1844. Concepción Bona was helped by her first cousin María de Jesús Pina.
Flag of Maldives. The colours used are Pantone 186 C for red and Pantone 348 C for green.
Used color: National flag | South African Government and Pantone Color Picker
| zelená | rendered as RGB 0 119 73 | Pantone 3415 C |
| žlutá | rendered as RGB 255 184 28 | Pantone 1235 C |
| červená | rendered as RGB 224 60 49 | Pantone 179 C |
| modrá | rendered as RGB 0 20 137 | Pantone Reflex Blue C |
| bílá | rendered as RGB 255 255 255 | |
| černá | rendered as RGB 0 0 0 |
Flag of Jamaica. “The sunshine, the land is green, and the people are strong and bold” is the symbolism of the colours of the flag. GOLD represents the natural wealth and beauty of sunlight; GREEN represents hope and agricultural resources; BLACK represents the strength and creativity of the people. The original symbolism, however, was "Hardships there are, but the land is green, and the sun shineth", where BLACK represented the hardships being faced.
bendera Indonesia
| Flag of Bolivia* | |
|---|---|
| country | Template:I18n/Republic of Bolivia |
| used by | Bolivia |
| from | 1851 |
| until | Present |
| created by | Government of Bolivia |
| format | 15:22 |
| shape | rectangular |
| colours | červená, žlutá, zelená
flag has 3 horizontal stripes |
| other characteristics | A horizontal tricolor of red, yellow and green. |
Note: The color selected is «turquoise blue» (the color mentioned in the decree), as defined by Pantone.
Flag of São Tomé and Príncipe
Flag of Namibia
Flag of Laos
Vlajka Angoly
Při zobrazení tohoto souboru lze snadno přidat orámování
Flag of Mauritania, adopted in 2017. The National Assembly added red stripes to the top and bottom edges to represent “the blood shed by the martyrs of independence”.
Flag of the Ivory Coast, written by Jon Harald Søby, modified by Zscout370. The colors match to what is reported at http://fotw.vexillum.com/flags/ci.html.
Flag of Togo. Aspect ratio modified for projects that require an aspect ratio of 3:2.
The national and official state flag of Haiti; arms obtained from File:Coat of arms of Haiti.svg. The civil flag can be found at here.
Flag of Rwanda. The flag ratio is 2:3 with the stripes being 2:1:1. Colors are the following officially: Pantone 299 C 2X (blue), RAL 6029 (green), RAL 1023 (yellow) and RAL 1003 (golden yellow). (As of 03/08/2010, the only color used is the Pantone 299 C, which is from here. The rest of the colors are RAL shades from here.)
Flag of Senegal
Vlajka Etiopie
Flag of Burkina Faso
The proportions of this flag are 3:2; however, there is no official definition for the correct proportions and also 5:3 is widely used.
The national flag of Nauru. Pantone 280c (Blue) and Pantone 123c (Yellow). On Pantone's official website these colours have the hexadecimal codes of #012169 and #FFC72C.
Flag of Gibraltar
The Flag of Vatican City State, as per the 2023 w:en:Fundamental Law of Vatican City State, reproducing Annex A which contains the official depiction of this version. See 2023 Fundamental Law of Vatican City State, art. 23, n. 1.
This 2023 flag is very similar to the flag used in the 1929 Fundamental Law of Vatican City State, see here, p. 35. Thus, it is in the public domain.
The Flag of Vatican City State, as per the 2023 w:en:Fundamental Law of Vatican City State, reproducing Annex A which contains the official depiction of this version. See 2023 Fundamental Law of Vatican City State, art. 23, n. 1.
This 2023 flag is very similar to the flag used in the 1929 Fundamental Law of Vatican City State, see here, p. 35. Thus, it is in the public domain.
Drapeaux de la France et de la Nouvelle-Calédonie côte-à-côte.
The flag of Guam, courtesy an e-mail from the author of xrmap. Modifications by Denelson83.
The flag of Aruba
Flago de la Kokosinsuloj, uzo ne oficiala
Flag of the Turks and Caicos Islands
The flag of Curaçao is a blue field with a horizontal yellow stripe slightly below the midline and two white, five-pointed stars in the canton. The geometry and colors are according to the description at Flags of the World.
Flag of Anguilla, adopted on 30 May 1990 and modified slightly on 25 January 1999.
The flag of the Pitcairn Islands, arms courtesy an e-mail from the author of xrmap and the Blue Ensign from Image:Government Ensign of the United Kingdom.svg
Autor: Allice Hunter, Licence: CC BY-SA 4.0
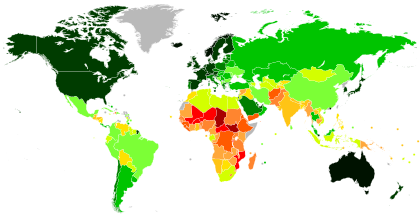
World map of countries or territories by Human Development Index scores in increments of 0.050 in 2021.
Drapeaux de la France et de la Nouvelle-Calédonie côte-à-côte.