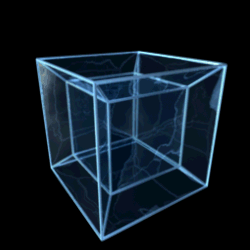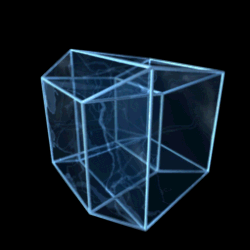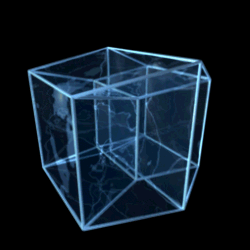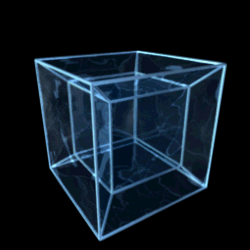
Teserakt
| Teserakt 8nadstěn | |
|---|---|
 3D projekce teseraktu | |
| Typ | Pravidelný polychoron |
| Nadstěn | 8 (4.4.4) |
| Stěn | 24 {4} |
| Hran | 32 |
| Vrcholů | 16 |
| Uspořádání vrcholů | 4 (4.4.4) (tetraedr) |
| Schläfliho symbol | {4,3,3} |
| Grupa symetrie | grupa [3,3,4] |
| Duální těleso | 16nadstěn |
| Vlastnosti | konvexní |
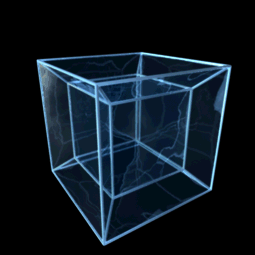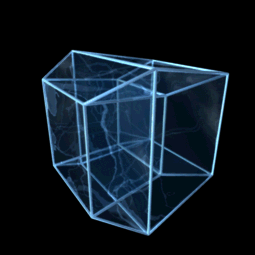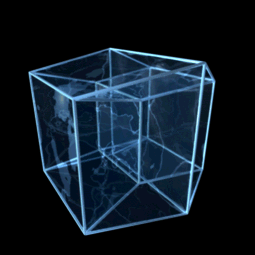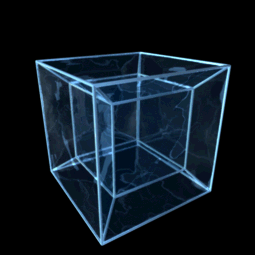
Teserakt či oktachoron je v geometrii čtyřrozměrnou analogií krychle, jde tedy o speciální variantu nadkrychle pro d=4. Odborněji by mohl být teserakt definován jako pravidelný konvexní čtyřúhelník s osmi krychlovými nadstěnami. Předpokládá se, že slovo teserakt vymyslel Charles Howard Hinton.
Geometrie
Standardní teserakt je v Euklidovském prostoru dán jako konvexní obal bodů (±1, ±1, ±1, ±1).
Objem a obsah teseraktu
Následující vzorce udávají, jaký je objem teseraktu, a jeho k-rozměrné povrchy (což je vždy obsah k-rozměrné stěny krát počet těchto stěn) v závislosti na hraně a.[1]
Poloměr vepsané koule je
a poloměr koule opsané je
 |  |  |
| d=2 | trojúhelník | čtverec | šestiúhelník | pětiúhelník |
| d=3 | čtyřstěn | krychle, oktaedr | krychloktaedr, kosočtverečný dvanáctistěn | dvanáctistěn, dvacetistěn |
| d=4 | 5nadstěn | teserakt, 16nadstěn | 24nadstěn | 120nadstěn,600nadstěn |
| d=5 | 5simplex | penterakt, 5ortoplex | ||
| d=6 | 6simplex | hexerakt, 6ortoplex | ||
| d=7 | 7simplex | hepterakt, 7ortoplex | ||
| d=8 | 8simplex | okterakt, 8ortoplex | ||
| d=9 | 9simplex | ennerakt, 9ortoplex | ||
| d=10 | 10simplex | dekerakt, 10ortoplex | ||
| d=11 | 11simplex | hendekerakt, 11ortoplex | ||
| d=12 | 12simplex | dodekerakt, 12ortoplex | ||
| d=13 | 13simplex | triskaidekerakt, 13ortoplex | ||
| d=14 | 14simplex | tetradekerakt, 14ortoplex | ||
| d=15 | 15simplex | pentadekerakt, 15ortoplex | ||
| d=16 | 16simplex | hexadekerakt, 16ortoplex | ||
| d=17 | 17simplex | heptadekerakt, 17ortoplex | ||
| d=18 | 18simplex | oktadekerakt, 18ortoplex | ||
| d=19 | 19simplex | ennedekerakt, 19ortoplex | ||
| d=20 | 20simplex | ikosarakt, 20ortoplex | ||
Teserakt v kultuře
Film
Teserakt se jednou zmiňuje ve filmu Interstellar, kdy robot TARS pronese větu: „Because the bulk beings are closing the tesseract. / Protože ty bytosti právě zavírají teserakt.“[2]
Externí odkazy
 Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu teserakt na Wikimedia Commons
Obrázky, zvuky či videa k tématu teserakt na Wikimedia Commons - HyperSolids je open source program pro Macintosh (Mac OS X a vyšší).
- Hypercube 98 Program pro Windows zobrazující animovanou 4D hyperkrychli vytvořený Rudy Ruckerem.
- Rozvinutý tvar 4D krychle obsahuje 5× + 17× obrázek
- 4D analogie krychle – popis konstrukce a vlastností teseraktu, včetně čtyřrozměrné Rubikovy kostky (3x3x3x3)
Reference
- ↑ FONTAINE, David A. Archivovaná kopie [online]. [cit. 2010-08-01]. Dostupné v archivu pořízeném dne 2004-07-02. (anglicky)
- ↑ (čas 2:33:40, titulky společnosti Netflix)
Média použitá na této stránce
This pseudo-projection of the tesseract or 4-dimensional cube is very similar to the vertex-first-projection. This diagram shows the tesseract as the 4-dimensional measure-polytope, is thus a 4-dimensional cartesian coordinate-system in its 2-dimensional representation.
The 4D-hypercube, layered according to distance from one corner.
As described in "Alice in Wonderland" by the Cheshire Cat, this vertex-first-shadow of the tesseract forms a rhombic dodecahedron.
The two central vertices would coincide in an orthogonal projection from 4 to 3 dimensions, but here they were drawn slightly apart.
| This SVG was created with Inkscape. |
Autor: Původně soubor načetl Tomruen na projektu Wikipedie v jazyce angličtina, Licence: CC BY-SA 3.0
Central projection of the tesseract, a Schlegel diagram

|
Držitel autorských práv k tomuto souboru, Robert Webb, dovoluje jeho užití komukoli pro jakýkoli účel, za podmínky, že je držitel práv správně uveden. Další šíření, tvorba odvozených děl, komerční využití i všechna další užití jsou dovolena. |
Uveďte autora:
Attribution must be given to Robert Webb's Stella software as the creator of this image along with a link to the website: http://www.software3d.com/Stella.php. A complimentary copy of any book or poster using images from the Software would also be appreciated where feasible.
|
The central projection of the four dimensional hypercube (tesseract or octahedroid) in 3D space.