Clonorchis sinensis LifeCycle
Causal Agent: The trematode Clonorchis sinensis (Chinese or oriental liver fluke).
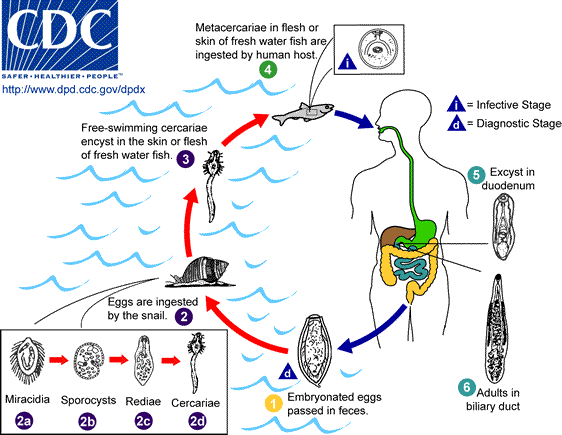
Life Cycle:
Life cycle of Clonorchis sinensis
Embryonated eggs are discharged in the biliary ducts and in the stool . Eggs are ingested by a suitable snail intermediate host ; there are more than 100 species of snails that can serve as intermediate hosts. Each egg releases a miracidia , which go through several developmental stages (sporocysts , rediae , and cercariae ). The cercariae are released from the snail and after a short period of free-swimming time in water, they come in contact and penetrate the flesh of freshwater fish, where they encyst as metacercariae . Infection of humans occurs by ingestion of undercooked, salted, pickled, or smoked freshwater fish . After ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum and ascend the biliary tract through the ampulla of Vater . Maturation takes approximately 1 month. The adult flukes (measuring 10 to 25 mm by 3 to 5 mm) reside in small and medium sized biliary ducts. In addition to humans, carnivorous animals can serve as reservoir hosts.
Geographic Distribution:
Endemic areas are in Asia including Korea, China, Taiwan, and Vietnam. Clonorchiasis has been reported in non endemic areas (including the United States). In such cases, the infection is found in Asian immigrants, or following ingestion of imported, undercooked or pickled freshwater fish containing metacercariae.Relevantní obrázky
Relevantní články
Motolice žlučováMotolice žlučová je trojhostitelská motolice parazitující v játrech člověka, prasete, šelem a potkanů. Je endemická na Dálném východě, kde infikuje odhadem 7 miliónů osob, v riziku je 260 miliónů lidí. Onemocnění způsobené touto motolicí se nazývá klonorchióza. Infekce touto motolicí má prokazatelný karcinogenní účinek na epitel žlučovodů a může vést ke vzniku nádorů žlučovodů (cholangiokarcinom). Proto byl druh v roce 2009 přiřazen k seznamu karcinogenů biologické povahy první kategorie. .. pokračovat ve čtení