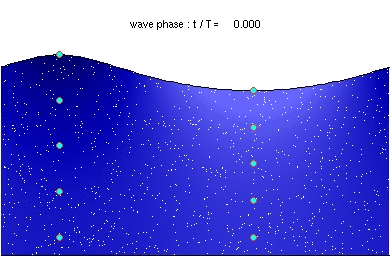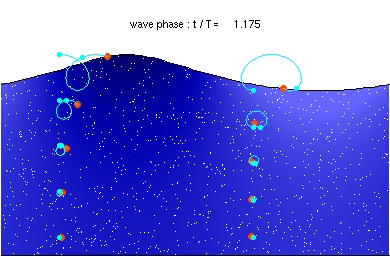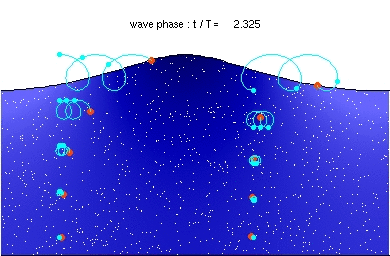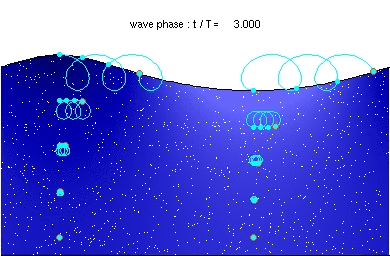
Deep water wave
Description of the animation: The red circles are the present positions of massless particles, moving with the flow velocity. The light-blue line gives the path of these particles, and the light-blue circles the particle position after each wave period. The white dots are fluid particles, also followed in time. In the case shown here, the mean Eulerian horizontal velocity below the wave trough is zero. Observe that the wave period, experienced by a fluid particle near the free surface, is different from the wave period at a fixed horizontal position (as indicated by the light-blue circles). This is due to the Doppler shift.
The wave physics are computed with the Rienecker & Fenton (R&F) streamfunction theory; for a computer code to compute these see: J.D. Fenton (1988) "The numerical solution of steady water wave problems". Computers & Geosciences 14(3), pp. 357–368. The animations are made from the R&F results with a series of Matlab scripts and batch files.Relevantní obrázky
Relevantní články
Mořská vlnaMořská vlna je pohyb částí vody. Vlny jsou vyvolávány především větrem a mořskými proudy. Mimoto mohou být vyvolány i zemětřesením, sesuvem půdy nebo části ledovce do vody apod. .. pokračovat ve čtení