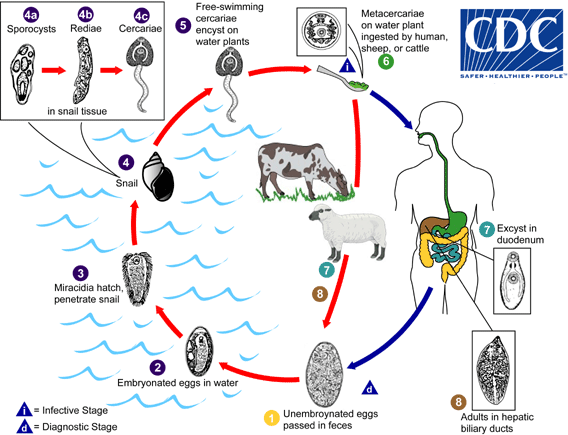
Fasciola LifeCycle
Causal Agents: The trematodes Fasciola hepatica (the sheep liver fluke) and Fasciola gigantica, parasites of herbivores that can infect humans accidentally.
Life Cycle:
Life cycle of Fasciola hepatica
Immature eggs are discharged in the biliary ducts and in the stool . Eggs become embryonated in water , eggs release miracidia , which invade a suitable snail intermediate host , including many species of the genus Lymnae. In the snail the parasites undergo several developmental stages (sporocysts , rediae , and cercariae ). The cercariae are released from the snail and encyst as metacercariae on aquatic vegetation or other surfaces. Mammals acquire the infection by eating vegetation containing metacercariae. Humans can become infected by ingesting metacercariae-containing freshwater plants, especially watercress . After ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum and migrate through the intestinal wall, the peritoneal cavity, and the liver parenchyma into the biliary ducts, where they develop into adults . In humans, maturation from metacercariae into adult flukes takes approximately 3 to 4 months. The adult flukes (Fasciola hepatica: up to 30 mm by 13 mm; F. gigantica: up to 75 mm) reside in the large biliary ducts of the mammalian host. Fasciola hepatica infect various animal species, mostly herbivores.
Geographic Distribution:
Fascioliasis occurs worldwide. Human infections with F. hepatica are found in areas where sheep and cattle are raised, and where humans consume raw watercress, including Europe, the Middle East, and Asia. Infections with F. gigantica have been reported, more rarely, in Asia, Africa, and Hawaii.Relevantní články
MotoliceMotolice jsou třída bezobratlých živočichů, kteří spadají do kmene ploštěnců (Platyhelminthes). Třída Trematoda (motolice) zahrnuje velkou skupinu helmintů, kteří se vyznačují nepřímým vývojem zahrnujícím 1–3 mezihostitele. Jedná se především o endoparazity obratlovců, jen malé množství druhů žije ektoparaziticky. Bylo popsáno více než 8000 druhů, přičemž řada z nich má velký medicínský či veterinární význam. Původně se třída Trematoda dělila do dvou podtříd Monogenea (jednorodí) a Digenea (dvourodí). V poslední době však převládl názor, že Monogenea se natolik odlišují, že byla vytvořena nová třída Monogenea.. .. pokračovat ve čtení