PIA19061-SaturnMoonEnceladus-CurtainNotDiscrete-Eruptions-20150506
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19061
Phantom jets in simulated images produced by the scientists line up nicely with some of the features in real images from NASA's Cassini spacecraft that appear to be discrete columns of spray.
Researchers modeled eruptions on Saturn's moon Enceladus as uniform curtains along prominent fractures that stretch across the icy moon's south pole. They found that brightness enhancements appear as optical illusions in places where the viewer is looking through a "fold" in the curtain. The folds exist because the fractures in Enceladus' surface are more wavy than perfectly straight. The researchers think this optical illusion is responsible for most -- but not all -- of what appear to be individual jets. Some discrete jets are still required to explain Cassini's observations.
Phantom jets in simulated images produced by the scientists line up nicely with some of the features in real Cassini images that appear to be discrete columns of spray. The correspondence between simulation and spacecraft data suggests that much of the discrete-jet structure is an illusion.
Curtain eruptions occur on Earth where molten rock, or magma, gushes out of a deep fracture. These eruptions, which often create spectacular curtains of fire, are seen in places like Hawaii, Iceland and the Galapagos Islands.
See PIA19060 for a related image and video animation.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and http://www.nasa.gov/cassini. The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org.Relevantní obrázky
Relevantní články
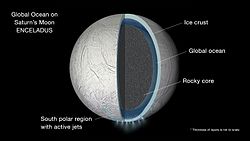
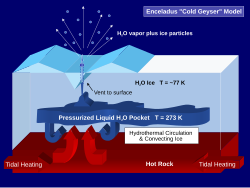
Enceladus (měsíc)Enceladus je šestý největší měsíc planety Saturn. Měsíc má v průměru téměř 500 kilometrů, což je přibližně desetina velikosti největšího měsíce Saturnu, Titanu. Enceladus je z většiny pokryt mladým a relativně čistým ledem, který odráží téměř veškeré sluneční světlo dopadající na jeho povrch. To má za následek extrémně nízkou teplotu povrchu pohybující se okolo -198 °C. I přes svou malou velikost se na Enceladu nachází celá řada povrchových útvarů od starších oblastí silně posetými impaktními krátery po novější útvary vzniklé v posledních 100 milionech let. Rozsáhlou geologickou aktivitu vyvolávají patrně slapové síly planety Saturn, podobně jako u Jupiterových měsíců Io a Europa, protože vlastní významné zdroje tepla z radioaktivního rozpadu mít Enceladus s ohledem na svou velikost nemůže. Předpokládá se, že k zahřívání přispívá i rezonanční vazba Enceladu s měsícem Dione v poměru 1 : 2, což vyvolává uvnitř obou měsíců dodatečné slapové síly, a spolupůsobit může i měsíc Mimas. Vliv slapových sil by však nestačil k roztavení ledu, proto se vědci domnívají, že nitro Encelada musí obsahovat i jiné těkavé látky s nízkým bodem varu. Na ledovém povrchu lze rozpoznat nejméně pět různých typů terénů: četné deformace, trhliny a prolákliny, ale jen málo impaktních kráterů, z nichž jsou mnohé přetvořené plastickým tečením povrchových vrstev měsíce. Největší kráter má průměr asi 35 km. Z jejich absence je tak zřejmé, že povrch je relativně mladý. .. pokračovat ve čtení