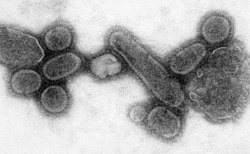
Reconstructed Spanish Flu Virus
- Photo Credit: Cynthia Goldsmith
- Content Providers(s): CDC/ Dr. Terrence Tumpey/ Cynthia Goldsmith
In order to sequester these virions, the MDCK cells were spun down (centrifugation), and the 1918 virus present in the fluid was immediately fixed for negative staining.
Dr. Terrence Tumpey, one of the organization’s staff microbiologists and a member of the National Center for Infectious Diseases (NCID), recreated the 1918 influenza virus in order to identify the characteristics that made this organism such a deadly pathogen. Research efforts such as this, enables researchers to develop new vaccines and treatments for future pandemic influenza viruses.
The 1918 Spanish flu epidemic was caused by an influenza A (H1N1) virus, killing more than 500,000 people in the United States, and up to 50 million worldwide. The possible source was a newly emerged virus from a swine or an avian host of a mutated H1N1 virus. Many people died within the first few days after infection, and others died of complications later. Nearly half of those who died were young, healthy adults. Influenza A (H1N1) viruses still circulate today after being introduced again into the human population in the 1970s.
|
This media comes from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Public Health Image Library (PHIL), with identification number #8243. Note: Not all PHIL images are public domain; be sure to check copyright status and credit authors and content providers.
|
Relevantní obrázky
Relevantní články
Španělská chřipkaŠpanělská chřipka je označení celosvětové chřipkové pandemie, která probíhala přibližně 2 roky, a to v letech 1918–1920. Způsobil ji virus chřipky A subtyp H1N1. Úmrtnost pandemie je odhadována na 1 až 5 % celkové populace, počet obětí se udává mezi 17 a 50, možná až 100 miliony, odpovídající 3 % až 10 % z nakažených lidí. Celkově šlo o jednu z nejsmrtonosnějších epidemií v dějinách lidstva. .. pokračovat ve čtení