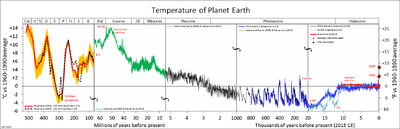
Temperature reconstruction last two millennia cs
The confidence interval incorporates two sources of uncertainty. The first one derives from the the method of translating information in the proxies into temperatures. Seven different peer-reviewed methods are employed and all considered equally likely in the figure. The methods range from a simple linear method where proxies sensitivities are fitted to the observational to determine past temperature, to more complicated methods in which information about spatial patterns is taken into account, or information about natural forcing is taken into account.
The second type of uncertainty is in the selection of proxies. Some proxies might not be entirely reliable and their inclusion might slightly bias the reconstruction. By randomly selecting a subset of proxies, this uncertainty can be quantified.
Code to create the figure is adapted from the Nature Geosciences paper[1] and can be found on https://figshare.com/collections/Global_mean_temperature_reconstructions_over_the_Common_Era/4507043. The figure is a simplification of Fig 1a from this paper. Individual reconstruction methods are not shown.
The observational data is HadCRUT5, plotted with a ten-year running mean.[3]
references
- ↑ a b PAGES 2k Consortium (2019). "Consistent multidecadal variability in global temperature reconstructions and simulations over the Common Era". Nature Geosciences 12. DOI:10.1038/s41561-019-0400-0.
- ↑ Pages2k Consortium (2017). "A global multiproxy database for temperature reconstructions of the Common Era". Scientific Data 4: 170088. DOI:10.1038/sdata.2017.88. ISSN 2052-4463.
- ↑ C.P. Morice et al (2021). "An Updated Assessment of Near-Surface Temperature Change From 1850: The HadCRUT5 Data Set". Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 126 (3): e2019JD032361. DOI:10.1029/2019JD032361. ISSN 2169-8996.
Relevantní obrázky
Relevantní články
Proxy dataProxy data jsou při studii historických průběhů klimatu – v tzv. paleoklimatologii nepřímé údaje, umožňující vědcům rekonstruovat klimatické podmínky, které panovaly v minulosti Země. Spolehlivé moderní záznamy o klimatu začínají až v roce 1880, proxy data poskytují vědcům údaje k určení klimatických modelů. Příkladem zdrojů pro proxy dat jsou ledovcová jádra, letokruhy, fosilní pyl, zkušební vrty, korály a mořské a jezerní usazeniny. Charakter depozice nebo rychlosti růstu materiálu byly ovlivněny klimatickými podmínkami v době, ve které se usazovaly nebo rostly. Také chemické stopy vytvořené klimatickými změnami, jako je množství jednotlivých izotopů, mohou být také použity pro proxy data. Některé proxy, jako například plynové bubliny uzavřené v ledu, umožňují zjišťovat složení dávné atmosféry, a dát tak svědectví o historickém kolísání složení zemské atmosféry. Pro zajištění přesných výsledků je třeba srovnávat jednotlivé metody zjišťování proxy dat. Velmi důležitá je také přesná práce a přesně vedené záznamy. .. pokračovat ve čtení