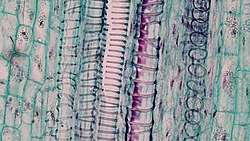
Woody Dicot Stem Ray System in One Year Quercus (35678974282)
cross section: One year Quercus stem magnification: 100x iron-alum hematoxylin and safranin stain
A cutinized epidermis overlays a two-layer cortex consisting of an outer zone of thick walled collenchyma and an inner zone of loosely packed parenchyma cells. During the first year of growth the underlying activity of the cork cambium begins to replace the epidermis and outer cortical tissues with a protective layer of cork rich periderm. Many cells in the periderm contain dark staining tannins.
Primary growth results in a ring of discrete vascular bundles that divides the parenchymatous cortex and pith. Xylem of each bundle is oriented towards the center of the stem and the phloem to the outside, with fascicular cambium in between. Phloem is heavily capped with sclerenchyma cells and sided by medullary parenchyma.
Due to meristematic activity the vascular bundles expand to form a cylinder consisting of a narrow outer ring of primary phloem, a middle single layered ring of vascular cambium and a deeper large ring of primary xylem. The phloem becomes overlaid by heavy continuous ring of sclerenchyma.
Bulging into the pith are small masses of the first xylem consisting of small protoxylem cells overlaid by a few larger, heavier walled cells of metaxylem. Above this and extending to the cambium are columns of primary xylem divided by narrow rays, extending from the large parenchymatous pith to the phloem.Relevantní obrázky
Relevantní články
StonekStonek je vegetativní orgán cévnatých rostlin a společně s kořeny a listy představuje hlavní stavební jednotku rostlinného těla. Charakter stonku a způsob jeho větvení určuje růstovou formu rostliny, tedy jedná-li se o strom, keř, bylinu, liánu a podobně. Stonek nese nad zemí listy a reprodukční orgány, pod zemí kořeny. Mimo to může plnit i řadu různých dalších funkcí. U většiny jednoděložných rostlin je stonek bylinný, u jehličnanů a většiny dvouděložných je druhotně tloustnoucí a více či méně dřevnatý. .. pokračovat ve čtení