GRACE globe animation
Gravity is determined by mass. Earth’s mass is not distributed equally, and it also changes over time.
The colors in this image represent the gravity anomalies measured by GRACE. One can define standard gravity as the value of gravity for a perfectly smooth 'idealized' Earth, and the gravity 'anomaly' is a measure of how actual gravity deviates from this standard. Red shows the areas where gravity is stronger than the smooth, standard value, and blue reveals areas where gravity is weaker. Red represents an acceleration of 5·10⁻⁴ m/s², blue represents -5·10⁻⁴ m/s², for a legend of the colors see File:Geoids sm.jpg.
GRACE is a collaborative endeavor involving the Center for Space Research at the University of Texas, Austin; NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.; the German Space Agency and the German Research Center for Geosciences, Potsdam.
More information on the GRACE mission is online at http://www.csr.utexas.edu/grace/ and http://grace.jpl.nasa.gov/.Relevantní obrázky
Relevantní články
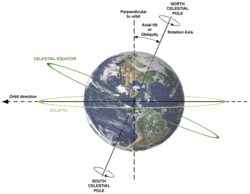
Zeměpisný pólZeměpisný pól, také geografický pól, je jeden ze dvou bodů na povrchu rotující planety nebo jiného rotujícího tělesa, kudy prochází pomyslná osa rotace. Poloha geografického pólu se může z důvodů nepravidelnosti otáčení planety v čase mírně měnit. Pozice zemských pólů se cyklicky mění v rozsahu několika metrů. Tento pohyb nelze zaměňovat s precesí. .. pokračovat ve čtení
Gravity Recovery and Climate ExperimentGravity Recovery A Climate Experiment (GRACE), je společným projektem NASA a německého Německého střediska pro letectví a kosmonautiku zabývající se podrobným měřením gravitačního pole Země a jeho místních anomálií. Projekt byl započat 17. března 2002, kdy byly z ruského kosmodromu Pleseck pomocí rakety Rokot vypuštěny 2 satelity. .. pokračovat ve čtení